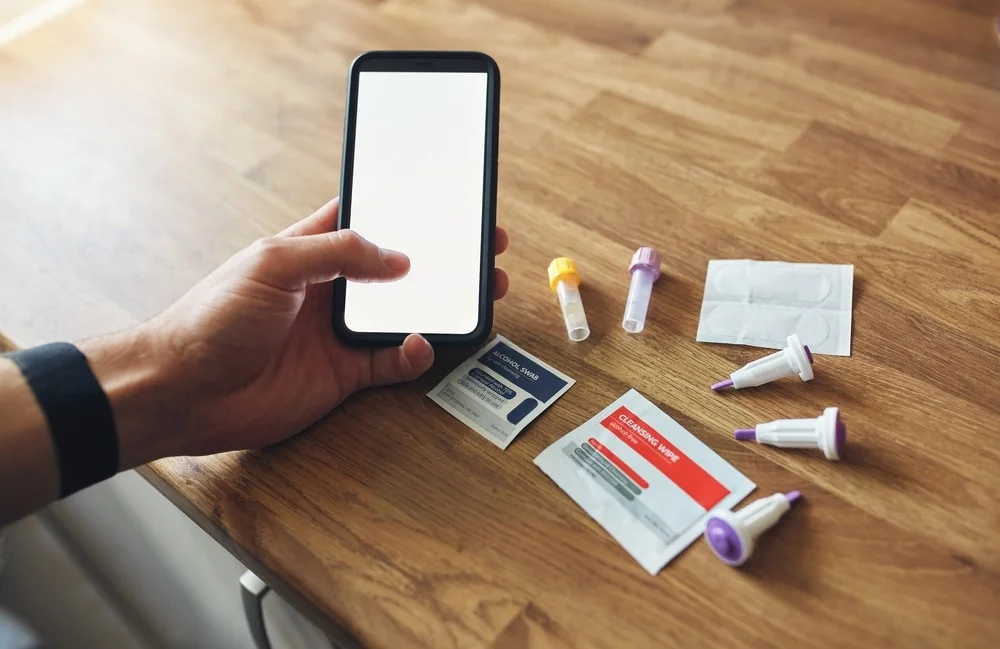
At-home test kits have revolutionized the way people monitor and manage their health. They provide individuals with the convenience of testing for various medical conditions in the comfort of their homes, without the need to visit a healthcare provider. These kits are available for a wide range of conditions, from pregnancy and diabetes to sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) and COVID-19. As technology has advanced, these tests have become more accessible, accurate, and easy to use, allowing users to take control of their health and make informed decisions.
The Evolution of At-Home Test Kits
The concept of at-home testing dates back to the mid-1970s when the first at-home pregnancy test kits were developed by Margaret M. Crane. These tests provided women with the ability to determine whether they were pregnant in the privacy of their own homes, eliminating the need for a visit to the doctor. Over the years, the technology behind at-home test kits has evolved significantly, allowing for a broader range of tests that are more accurate and user-friendly.
In recent years, there has been a surge in the popularity of at-home tests for various medical conditions. These tests are now available for conditions such as food allergies, ovulation, diabetes, respiratory viruses, and even some types of cancer. This growth in demand can be attributed to the increasing awareness of health issues, the desire for privacy and convenience, and the ongoing advancements in medical technology.
Types of At-Home Test Kits
At-home test kits generally fall into two categories: self-tests and self-collection tests.
- Self-Tests: Self-test kits require individuals to collect samples—such as blood, urine, or saliva—and apply them to the testing device as instructed. The test will then provide immediate results, usually within a few minutes. Common examples of self-test kits include pregnancy tests, blood glucose monitors for diabetes, and cholesterol tests.
- Self-Collection Tests: Self-collection test kits allow users to collect samples at home, which are then sent to a laboratory for analysis. After the laboratory evaluates the sample, the results are sent to the user via email, post, or directly to their healthcare provider. These tests are often used for more complex analyses, such as genetic tests, STD screenings, or cancer markers.
Both types of kits offer the advantage of convenience, as they can be completed at any time and without the need for a doctor’s appointment. However, self-collection tests tend to be more accurate because the samples are analyzed in a controlled laboratory environment.
How At-Home Test Kits Work
One of the most common technologies used in at-home test kits is lateral flow assays (LFA). This technology is often used in self-test kits to detect a variety of biomarkers. The principle behind LFA is simple yet effective: a liquid sample (such as saliva, urine, or blood) containing the biomarker moves through a test strip via capillary action. The polymeric materials in the strip interact with the biomarker, and this interaction is detected through a visual signal, such as a color change or the appearance of a line on the test strip.
In some cases, more sophisticated versions of LFA are used, including lateral flow immunoassays (LFIAs) and nucleic acid lateral flow assays (NALFA). These tests can detect more complex biomarkers, such as antibodies or genetic material from viruses, which are crucial for diagnosing conditions like COVID-19 or sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
To enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of these tests, many use advanced reagents, such as nano-gold microspheres or immune-nanoparticles. These reagents amplify the signal, making it easier to detect the presence of the target biomarker. Some kits also employ thermal contrast, laser, or LED technology to further boost detection capabilities.
The Development and Regulation of At-Home Test Kits
The development of at-home test kits is regulated by various international health authorities to ensure their safety and effectiveness. Manufacturers must comply with strict regulations, especially for more sensitive tests, such as HIV or genetic tests. In the UK and European Union, for example, self-test diagnostic devices are independently reviewed by notified bodies, like the British Standard Institution (BSI) or the Technischer Überwachungsverein (TÜV), before being made available for sale. These bodies assess the safety, accuracy, and reliability of the devices before they can be sold to the public.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) plays a critical role in regulating self-test kits. The FDA approves the kits based on their clinical validity, ensuring that they produce accurate results and meet safety standards. Test kits that have been FDA-approved can be trusted to provide reliable results, as long as users follow the instructions correctly.
Popular At-Home Tests and What They Can Detect
There is a wide range of conditions that can be monitored or diagnosed using at-home test kits. Here are some examples of the most common tests available today:
- Pregnancy Tests: These tests detect the presence of the human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) hormone in urine, which is produced during pregnancy. They provide quick results, usually within a few minutes.
- Blood Glucose Tests: These tests measure the amount of glucose in your blood and are essential for managing diabetes. Regular blood glucose testing helps people with diabetes monitor their condition and adjust their treatment plan accordingly.
- Cholesterol Tests: At-home cholesterol tests can measure your total cholesterol, HDL (good cholesterol), and LDL (bad cholesterol) levels. High cholesterol is a significant risk factor for heart disease, making these tests essential for cardiovascular health.
- COVID-19 Tests: These tests detect the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, either by identifying viral RNA or by detecting antibodies that indicate past infection. These tests have become incredibly important during the COVID-19 pandemic, providing individuals with an easy way to determine whether they are infected.
- STD Tests: At-home STD tests can screen for various sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, and HIV. These tests often involve urine samples, blood samples, or vaginal swabs.
- Food Allergy Tests: These tests measure the presence of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in the blood, which can indicate an allergic reaction to certain foods.
- Vitamin and Hormone Tests: Some at-home test kits can measure specific vitamins and hormone levels in the blood, such as vitamin D, which is crucial for bone health, or thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism.
- Colorectal Cancer Screening: At-home kits are also available to test for early signs of colorectal cancer. These tests often detect blood in stool samples, which can indicate the presence of cancer or precancerous conditions.
Benefits and Drawbacks of At-Home Test Kits
Benefits:
- Convenience: At-home test kits allow individuals to test themselves in the privacy and comfort of their own homes, avoiding the need for doctor’s appointments or visits to the clinic.
- Early Detection: Many at-home tests can detect conditions before symptoms appear, which allows for early intervention and better outcomes.
- Privacy: Some individuals may feel embarrassed about seeking medical attention for certain conditions, such as STDs. At-home tests eliminate this barrier and allow for more comfortable testing.
- Cost-Effective: Many at-home test kits are more affordable than seeking medical attention or lab tests, especially when used for routine monitoring.
Drawbacks:
- Accuracy: While most at-home test kits are reliable, there is always the potential for false positives or false negatives. This can lead to unnecessary worry or missed diagnoses.
- Limited Scope: At-home test kits cannot replace professional medical evaluations. In many cases, a more comprehensive diagnosis requires a visit to a healthcare provider.
- Emotional Stress: Receiving a positive result from an at-home test can be stressful, especially if you are unsure how to proceed. It’s important to remember that a positive result does not always mean you have a serious condition.
How to Ensure Reliable Results from At-Home Test Kits
To get the most accurate results from your at-home test kits, it’s essential to follow the instructions carefully. Here are some tips to ensure the reliability of your results:
- Choose FDA-Approved Kits: Only use test kits that have been approved by regulatory authorities, such as the FDA in the United States or the MHRA in the UK. These kits have undergone rigorous testing to ensure their accuracy and safety.
- Follow the Instructions: Read and follow the instructions on the test kit carefully. Even minor errors, such as using an expired kit or misapplying a sample, can lead to inaccurate results.
- Consider False Positives and Negatives: Keep in mind that no test is perfect. If you get a positive result, consider consulting a healthcare professional for confirmation. Similarly, if you get a negative result but still have symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice.
- Keep Track of Expiration Dates: Always check the expiration date on the test kit before using it. Expired kits may not work properly, leading to inaccurate results.
At-home test kits have made it easier than ever to monitor and manage a wide range of health conditions from the comfort of home. These tests offer numerous benefits, including convenience, privacy, and early detection. However, it’s important to understand the limitations of these tests and consult with a healthcare provider when necessary. With the right precautions and proper use, at-home test kits can be an invaluable tool in maintaining your health and wellbeing.