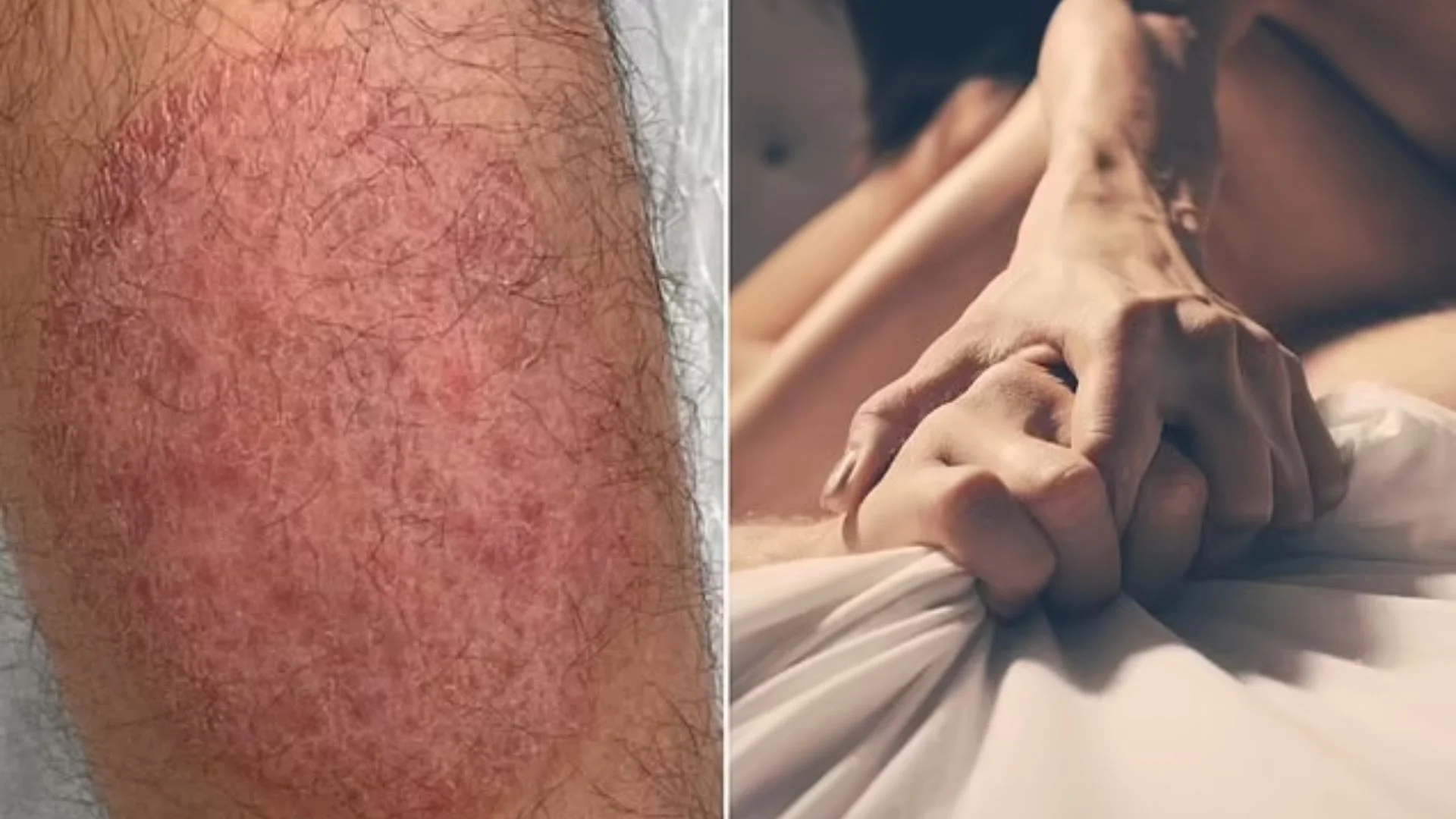
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported an outbreak of a rare and highly contagious fungal infection in New York, known as “jock itch.” The infection, caused by the Trichophyton mentagrophytes genotype VII (TMVII) fungus, results in an itchy, scaly rash that can appear on the trunk, groin, genitals, or face. Since the first reported case in June, four more cases have been confirmed.
TMVII spreads primarily through sexual contact and can lead to severe symptoms, including inflammation and a painful rash. In some cases, the condition may also cause secondary bacterial infections.
According to a CDC statement, all four currently affected patients are cisgender men between the ages of 30 and 39, with recent sexual contact among men. Two of the men reported direct sexual contact, while the other cases have no known epidemiological links. One patient is a sex worker, and another reported recent travel to Europe, while the others reported no recent international travel.
The CDC has alerted healthcare professionals, particularly dermatologists, to recognize TMVII as a possible sexually transmitted infection. The infection, known medically as tinea cruris, is treatable with antifungal medications, although full recovery may take several months. The use of antifungal creams, ointments, or powders can help manage symptoms within 2 to 4 weeks, though extended treatment may be necessary in some cases.