The thyroid, a small butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck significantly contributes to our well-being. Responsible for hormones that regulate metabolism and growth, the thyroid gland plays a pivotal role in human development. However, a shadow casts over this gland, affecting a staggering 200 million people globally. The urgency to address this health challenge is underscored by the fact that, as of now, half of the global population remains undiagnosed for thyroid disorders, a condition more common among women and the elderly. In India, where 30% of the population is female, thyroid disease poses a significant health challenge for women.
Decoding the gender bias
Women navigate a complex journey of hormonal changes, marked by both pre and postmenopausal stages. These transitional phases often coincide with a higher frequency of hypothyroidism and thyroid nodules. Pregnancy introduces additional complexities, as hormonal shifts during this period can impact thyroid function. Moreover, the female hormone, estrogen, is closely connected to a key thyroid hormone called thyroxine.
This connection is crucial at different stages of life like puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, making women more likely to have issues with their thyroid. Recognizing how clinical symptoms change with age is crucial, as it is more noticeable in women over the age of 50, showing the importance of understanding how thyroid problems change as women get older.
Autoimmune nature: A double-edged sword
Another layer to the gender disparity in thyroid disorders lies in their autoimmune nature. Many thyroid disorders, including the common hypothyroidism and thyroid nodules, have an autoimmune component. The immune system, in its misguided defense, can turn against the thyroid gland, leading to disruptions in its normal functioning. This autoimmune aspect contributes significantly to the elevated prevalence of thyroid disorders in women.
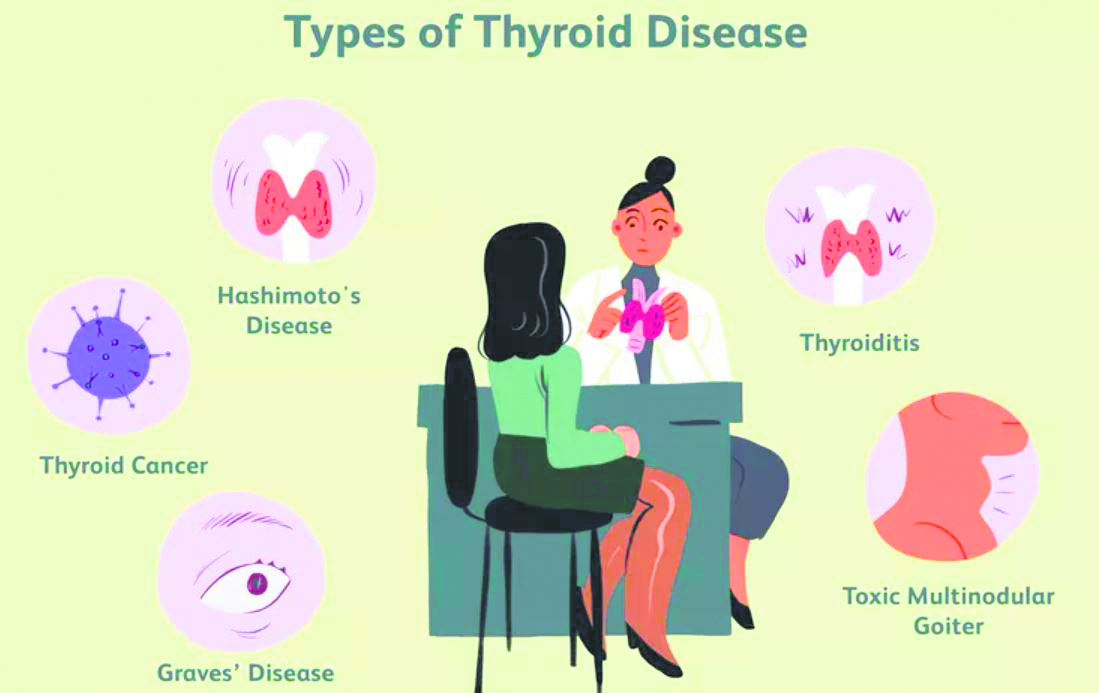
Symptoms and types of thyroid disorders
Recognising thyroid disorders are vital, given their subtle yet impactful symptoms. Joint pain, weight gain, dizziness, infertility, fatigue, and increased sensitivity to colds are some of the common indicators. Besides, understanding different types of thyroid disorders- hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid nodules, and thyroid cancer- is key to early diagnosis and effective management. Among the diverse types of thyroid disorders, hypothyroidism stands out as the most prevalent issue observed in women.
Role of Homeopathy in treating thyroid disorders
Unlike conventional treatments, Homeopathy emerges as a holistic and side-effect-free approach. This complementary medical system, renowned for determining the root causes, assures effective and long-lasting treatment without creating a lifelong dependency on medications or surgeries. Homeopathic remedies
Thyroidinum is recommended for individuals with facial puffiness and weight gain concerns, while CalcareaCarbonica proves effective for addressing excessive weight gain related to thyroid issues. Natrum Mur is known for its efficacy in addressing specific complaints associated with hypothyroidism, including depression, hair thinning, and hair loss. Graphites is a suitable remedy for hypothyroid patients who are both significantly obese and overly sensitive to cold.
Natural tips for hypothyroidism management
Beyond medical interventions, adopting natural strategies becomes imperative. Maintaining a healthy weight, correcting iodine deficiencies, addressing vitamin and mineral imbalances, managing stress, and maintaining hormonal balance are integral components of a holistic approach to managing hypothyroidism. Always consult with a qualified homeopath for hypothyroidism.
The author is a Padmashree recipient, and the founder and chairman of DrBatra’s Healthcare