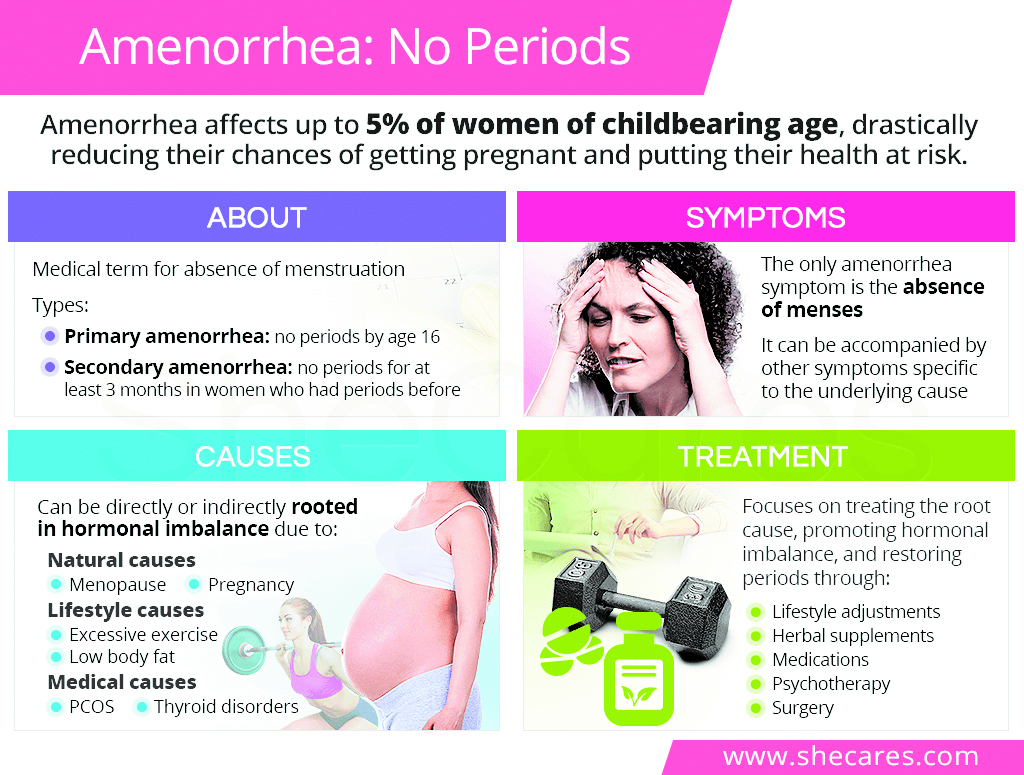
Amenorrhea is a medical term used to describe the absence of menstrual periods in females who should be menstruating. It affects both teenage girls and women of reproductive age. A critical reason of this medical condition is that the ovaries of the majority of amenorrheic women do not release an egg and are unable to get pregnant.
For a more comprehensive understanding of amenorrhea, these can be classified into two main types: primary and secondary amenorrhea. Primary amenorrhea occurs when a girl has not started menstruating by the age of 16 years.

The causes for the same can occur due to factors like genetic problems, hormonal imbalances (most frequent), anatomical abnormalities of the reproductive organs, or chronic illnesses.
On the other hand, secondary amenorrhea refers to the absence of three or more periods in a row in women who have previously menstruated for at least several months. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including pregnancy, breastfeeding, extreme weight loss or gain, stress, intense exercise, hormonal imbalances, thyroid disorders, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and certain medications.
Symptoms of Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea involves several symptoms that may indicate an underlying cause. These symptoms include changes in breast tissue, changes in body hair, hair loss, vaginal dryness, pelvic pain, changes in libido, excess facial hair, and acne.
Causes
Amenorrhea can be caused by several circumstances occurring naturally, while others are a side effect of medicine or an indication of a medical problem. Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause are some of the natural causes of amenorrhea.
Hormonal Imbalances: Particularly those involving estrogen and progesterone, can disrupt the menstrual cycle and cause amenorrhea.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common hormonal illness caused by irregular menstrual cycles, ovarian cysts, and hormonal imbalance.
Premature Ovarian Failure (POF): Also known as premature menopause, it develops when a woman’s ovaries refuse to function before the age of 40, resulting in amenorrhea and infertility.
Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt the menstrual cycle, resulting in amenorrhea. Both conditions result in an imbalance of thyroid hormones, which are crucial in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and various bodily functions.
Stress: Physical or mental stress can disrupt the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis, resulting in amenorrhea. Stress-related amenorrhea is commonly observed in women who experience intense emotional stress, such as major life changes, psychological trauma, or eating disorders
Excessive Exercise: Intense physical activity can affect hormone levels due to the physiological stress on the body.
Diagnosis and Treatment
One should consult a doctor if they missed three periods in a row or if they are 16 years old and have not begun menstruation. It could be an indication of an underlying medical condition that requires care. Diagnosing the underlying cause of amenorrhea typically involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests.
These may include blood tests to assess hormone levels, imaging studies such as ultrasounds or MRI scans to evaluate the reproductive organs, and other specialized tests as deemed necessary by a healthcare professional. Certain lifestyle changes may be advised, such as food adjustments, stress management techniques, or workout regimen adaptations.
Menstrual cycle regulation and hormonal balance restoration may require prescriptions for hormonal therapy, such as birth control tablets or hormone replacement therapy. Thus, women having amenorrhea should consult a doctor for a thorough diagnosis and obtain individualized care that is suited to their requirements.
Menstruation could be discontinued for a variety of triggers. It does not necessarily imply that a person is infertile and cannot conceive. However, it is suggestive that women should go for an early diagnosis to address underlying issues that can restore regular menstrual cycles, promoting optimal reproductive health and overall wellness. Also starting treatment in time to prevent complications .
Dr. C S Mythreyi, Senior Consultant, Obstetrics & Gynecologist
Madhukar Rainbow Children’s Hospital, Delhi