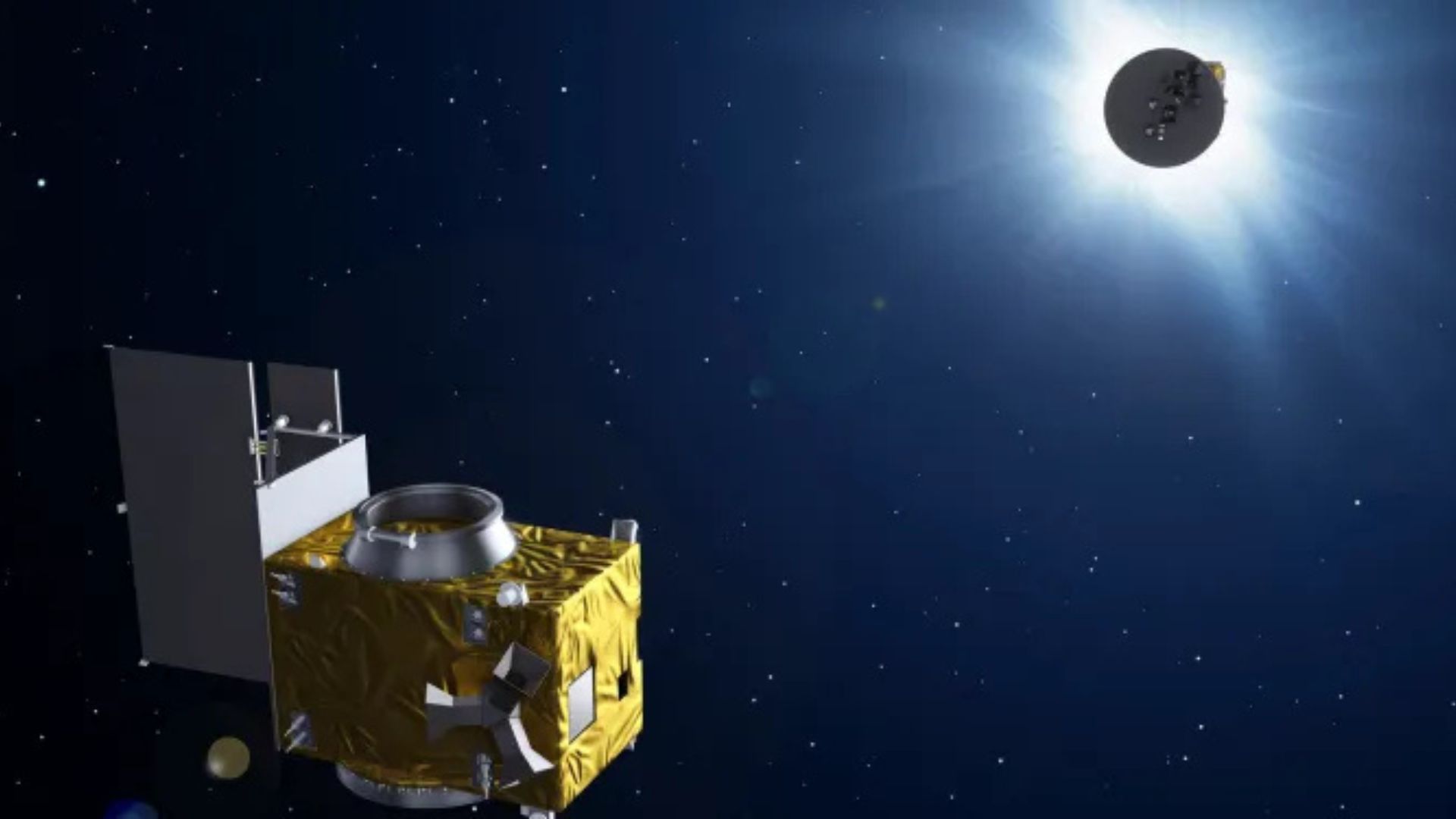
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced the launch of the PSLV-C59/PROBA-3 mission, scheduled for December 4 (Wednesday) at 4:06 PM from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh. This mission will see the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)-C59 carrying satellites weighing approximately 550 kg into a highly elliptical orbit.
The PROBA-3 mission is an “In-Orbit Demonstration (IOD) mission” developed by the European Space Agency (ESA).
⏳ 2 Days Left!
The PSLV-C59/PROBA-3 Mission, the 61st flight of PSLV and the 26th using PSLV-XL configuration, is set to carry ESA’s PROBA-3 satellites (~550kg) into a highly elliptical orbit.
💡 PSLV-C59 Configuration:
Stages: 6PSOM-XL + S139 + PL40 + HPS3 + L2.5
Liftoff… pic.twitter.com/7B9sSkGeb4— ISRO (@isro) December 2, 2024
Highlighting the upcoming launch on X, ISRO stated, “The PSLV-C59/PROBA-3 Mission, the 61st flight of PSLV and the 26th using PSLV-XL configuration, is set to carry ESA’s PROBA-3 satellites (~550kg) into a highly elliptical orbit.”
“The mission goal is to demonstrate precise formation flying,” ISRO added in its statement. The mission will involve two spacecraft, the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC) and the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC), launched together in a “stacked configuration” (one atop the other).
Must Read: Allahabad High Court To Hear Gyanvapi Survey Plea On December 10
PSLV, India’s first launch vehicle equipped with liquid stages, has been instrumental in carrying satellites and other payloads into space according to ISRO’s requirements. The PSLV’s first successful launch took place in October 1994. According to ISRO, the PSLV-C59 mission will involve four stages of launch, with the vehicle lifting a total mass of approximately 320 tonnes.
ISRO also emphasized the precision and collaborative nature of this mission, stating, “This mission exemplifies the trusted precision of PSLV and the collaboration of NSIL (NewSpace India Limited), ISRO, and ESA.”
The previous PSLV mission, PSLV-C58, successfully launched the XPOSAT satellite into an Eastward low-inclination orbit on January 1, 2024. XPOSAT, also known as the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite, was India’s first dedicated scientific satellite to conduct space-based polarisation measurements of X-ray emissions from celestial sources.