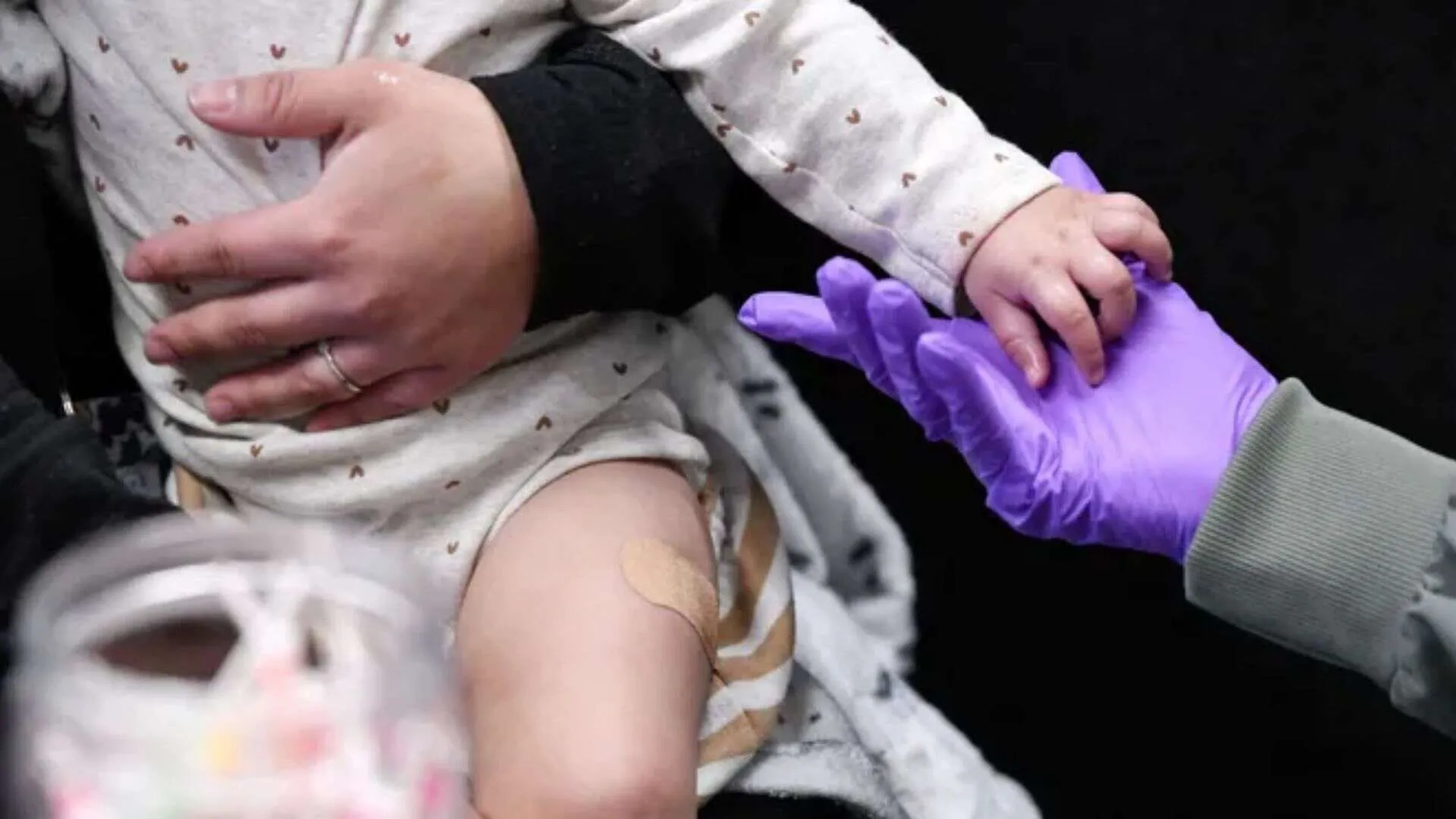
A large measles outbreak has hit the U.S., with 607 cases—almost double those of 2024. Most cases are in Texas, with 505, and involve two deaths of unvaccinated children in rural West Texas. The outbreak highlights the risk of low vaccination rates in a number of states.
Since January, Texas has confirmed 505 cases of measles in 21 counties, with the hardest-hit county being Gaines County. There have been one new hospitalization and one death of an 8-year-old child confirmed by health officials. The majority of cases in Texas are among the underserved Mennonite population, and the outbreak also crosses into surrounding New Mexico.
States Impacted by the Outbreak
The outbreak isn’t limited to Texas. There are other states such as New Mexico, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Ohio with cases, including New Mexico having 56 cases confirmed. There have been cases in Kansas and Oklahoma attributed to the Texas and New Mexico outbreaks.
Measles Outbreak Spreads Across U.S.
The CDC announces clusters of measles in several U.S. states, such as Indiana, California, Florida, and Michigan, with more than six active outbreaks. The virus tends to spread where there is low vaccination, and the U.S. already has 607 cases this year.
Recommended Vaccination
To avoid measles, health professionals recommend the MMR vaccine, complemented by booster shots for at-risk individuals, particularly in cases of outbreaks. Past vaccination or immunity means not requiring the vaccine, but doubtful individuals regarding vaccination status can undergo a booster.
Symptoms and Treatment of Measles
Symptoms of measles are high fever, cough, runny nose, red eyes, and rash. While most children will recover, pneumonia and swelling of the brain can occur. There is no treatment, so doctors control symptoms.Measles Outbreak Shakes US with 607 Cases, 505 Reported in Texas
Pandemic vaccination coverage has declined, which has broken herd immunity and enabled measles to spread more freely. Increased vaccination coverage, particularly at 95% or higher, is needed to avoid further outbreaks and safeguard communities.