The connection between health and wealth becomes more apparent as people age. Ageing, a natural process we all experience, brings increased susceptibility to chronic conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis. Cognitive decline, vision and hearing issues, and a higher risk of falls and fractures are also common concerns among the elderly. With the rapid ageing of society, the number of older adults facing these challenges is rising. In India, the situation is particularly critical, with the population aged 60 and above projected to increase to 319 million by 2050 from 100 million in 2011. This demographic shift underscores the urgent need for effective support systems for the elderly, as not everyone benefits equally from social and economic improvements that contribute to longer lifespans.
The Importance of Chronic Disease Management for the Elderly
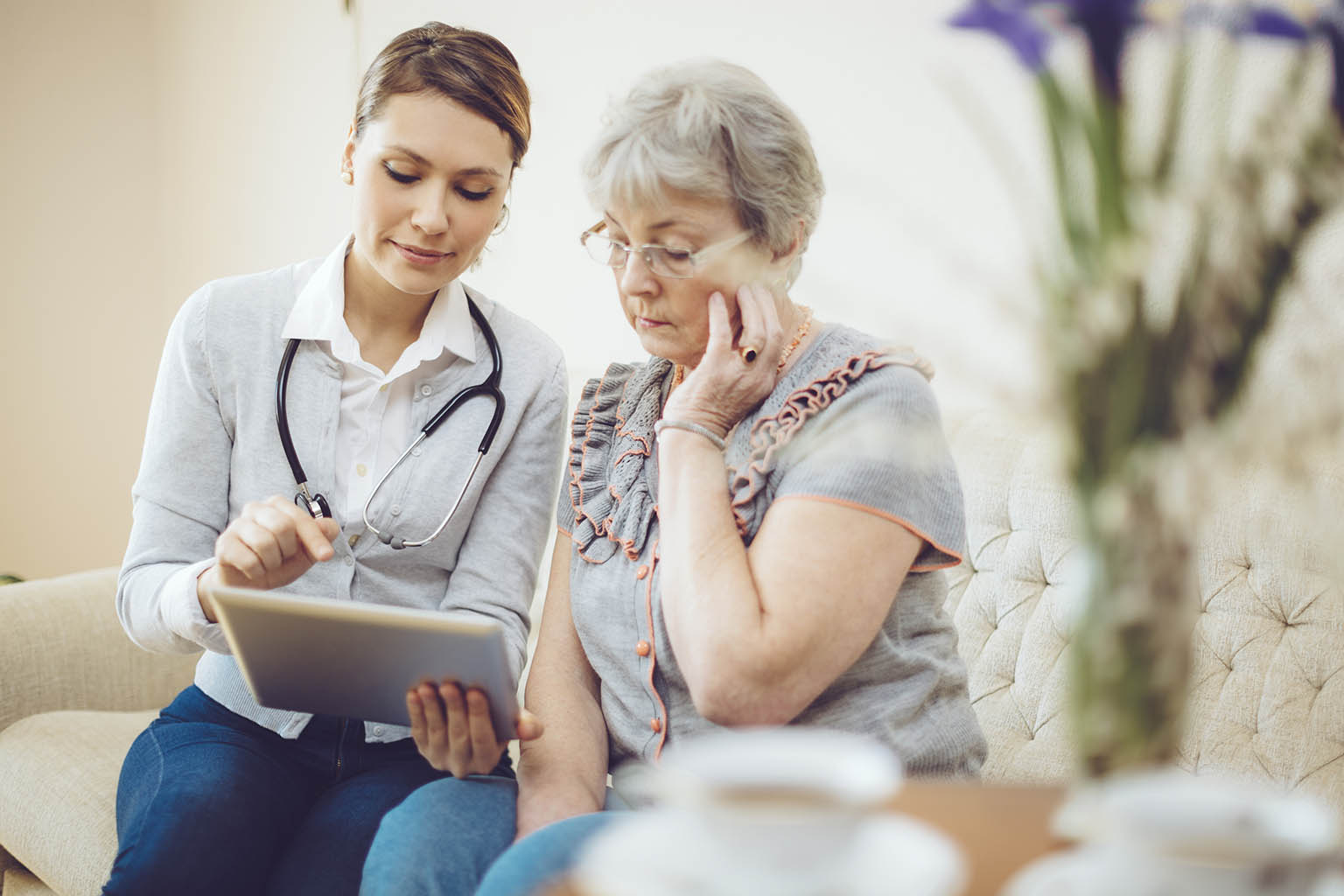
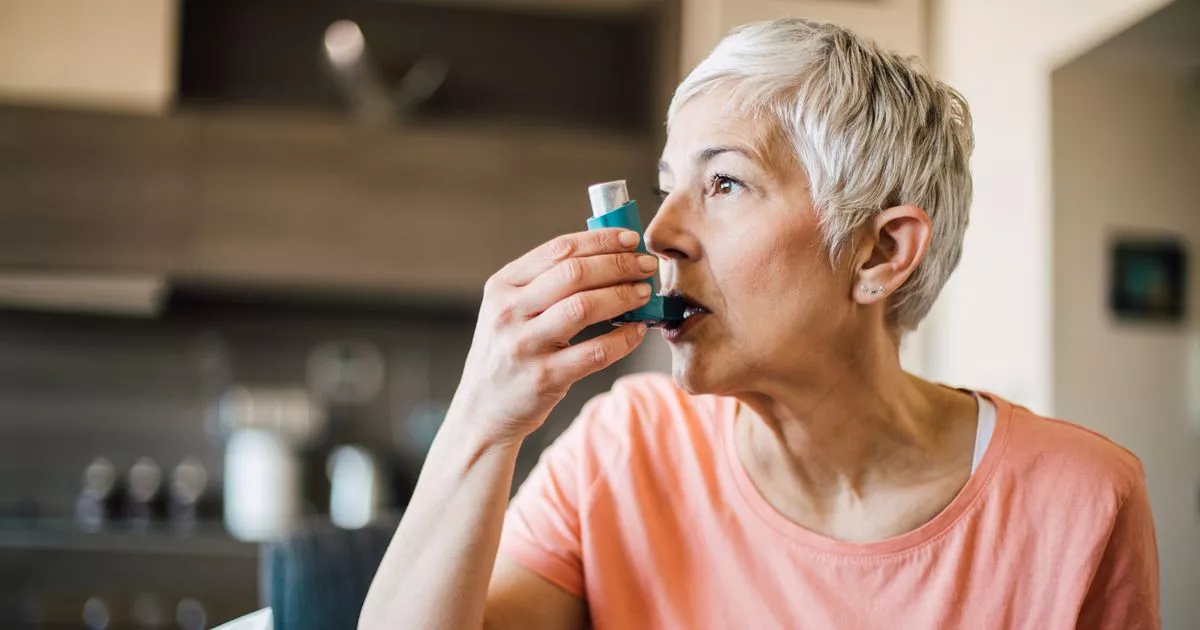
Chronic diseases are a leading cause of death globally, accounting for 74% of all deaths, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Older adults are particularly vulnerable, often suffering from multiple chronic conditions, such as hypertension, arthritis, coronary heart disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and more. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that 85% of older adults have at least one chronic condition, and 60% have two or more. This highlights the critical need for prioritizing health and implementing effective management strategies for this demographic.
Understanding the Challenges
Older adults in India face numerous challenges, including social isolation, financial insecurity, and limited access to essential resources. Despite advancements in healthcare, many elderly individuals struggle to access adequate medical care due to financial constraints, as most rely on pensions, and geographic barriers further exacerbate the issue. Depression, anxiety, and other mental health problems are common among the elderly, significantly impacting their quality of life. Changes in family structure, such as the death of a spouse or children moving away, contribute to feelings of loneliness and depression. This social isolation can limit their engagement in activities of interest, further complicating the management of chronic conditions. Additionally, older adults are often targeted by scams, leading to financial and emotional distress, which hinders their ability to afford necessary healthcare.
Strategies for Managing Chronic Diseases in Older Adults
- Positive Communication: Effective communication is crucial in managing elderly patients. Caregivers and healthcare providers must engage in active listening, encourage questions, and show compassion to ensure that health issues are detected early and managed effectively.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Frequent medical check-ups are essential for managing chronic conditions. Senior health clinics provide reliable care for elderly individuals with chronic diseases. Regular visits help control existing conditions and reduce the risk of developing new ones.
- Detailed Medical Records: Maintaining detailed medical records is vital for elderly patients with multiple chronic conditions. These records enable healthcare professionals to understand the patient’s history, facilitate quick diagnosis and treatment, and coordinate care among various providers.
- Clean and Safe Environment: A clean environment, combined with a healthy diet and adequate sleep, plays a significant role in the well-being of older adults. Understanding the dynamics of chronic conditions helps create an environment conducive to managing the disease. For instance, Alzheimer’s and dementia patients benefit from familiar surroundings and experienced healthcare staff.
The Role of Government and Community
Improving the lives of the elderly requires strong government policies and community support. The National Policy on Older Persons (1999), the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act (2007), the National Policy for Senior Citizens (2011), and the National Programme for Health Care of Elderly under the Ayushman Bharat program provide a legal framework for supporting the elderly in India. As a community, it is our responsibility to provide adequate community centers, volunteer services, and social functions for the elderly.
The support of the community, coupled with proactive health measures, ensures that seniors spend their golden years with dignity, purpose, and fulfillment. As India’s population ages, the focus must shift from viewing this demographic shift as a challenge to recognizing the opportunities for resilience, inclusivity, and growth.
Sama Beg is the Chief Product Officer at Emoha.