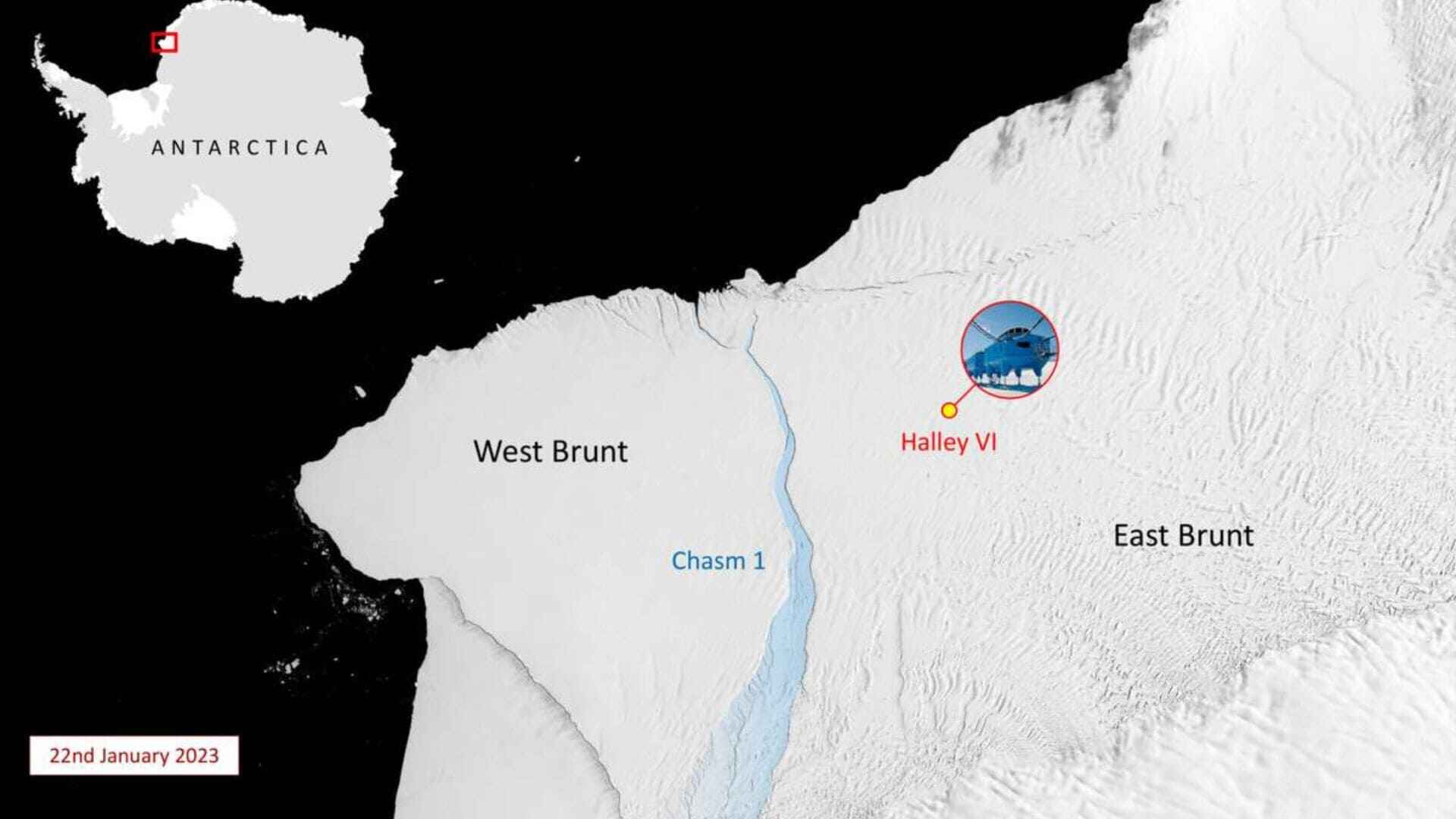
A significant iceberg, measuring approximately 380 square kilometers — roughly the size of the UK’s Isle of Wight and nearly equivalent to Amsterdam — has fractured from Antarctica, near the UK’s Halley research base. This marks the third such iceberg to detach from the area in the past three years. The separation occurred subsequent to the emergence of a 14-kilometer-long fissure, branching off at a 90-degree angle from the existing Halloween Crack, with the final split taking place in the early hours of May 20.
The British Antarctic Survey, responsible for monitoring the region, documented this calving event. While there’s no direct evidence linking these occurrences to climate change, they underscore the dynamic nature of the Brunt Ice Shelf, home to Halley. Concerns about ice behavior prompted the relocation of the research facility in 2017, with operations limited to the Antarctic summer, spanning from November to March.
Dr. Oliver Marsh, a seasoned glaciologist, highlighted that iceberg calving, though natural, can dramatically reshape ice shelf geometry and influence local ocean currents. Continuous monitoring is crucial for ensuring safety and sustaining scientific endeavours at Halley.
Professor Adrian Luckman from Swansea University emphasized that even in Antarctica’s frigid regions, such calving events are becoming more frequent. Understanding these processes is essential for predicting future changes in ice shelves and their potential impact on global sea levels.
The Brunt Ice Shelf’s ongoing activity provides valuable data for researchers aiming to comprehend the mechanisms driving iceberg calving and anticipate the future evolution of these vital ice formations. As scientists delve deeper into these phenomena, they aim to gain insights into broader climate dynamics and their implications for our planet’s future.















