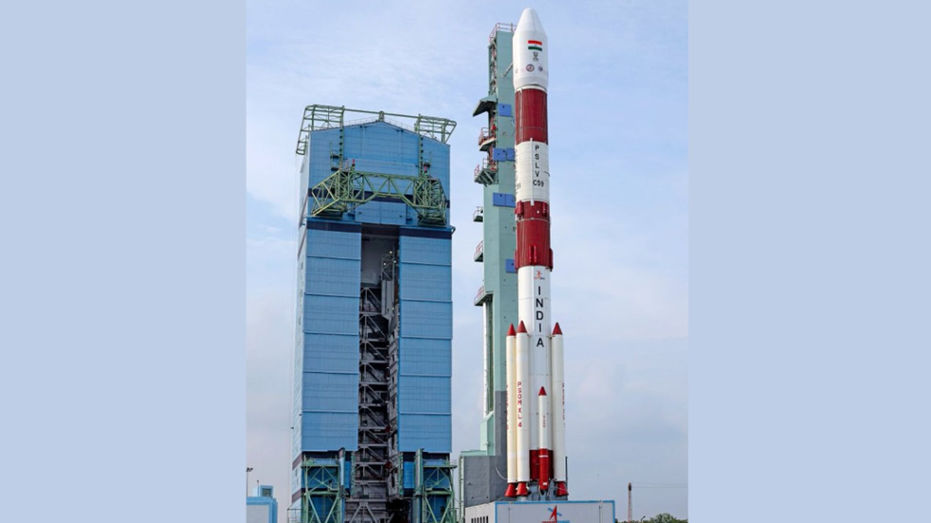
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is preparing for the launch of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV)-C59 / Proba-3 mission from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, on Wednesday. This launch marks a significant milestone in India’s space journey.
Mission Overview
PSLV-C59 will carry satellites weighing around 550 kg into a highly elliptical orbit. Moreover, the Proba-3 mission is an “In-Orbit Demonstration (IOD)” mission by the European Space Agency (ESA), showcasing advanced space technologies.
Spacecraft to be Launched
The mission involves two spacecraft: the Coronagraph Spacecraft (CSC) and the Occulter Spacecraft (OSC). Both spacecraft will be launched in a stacked configuration, one on top of the other, ensuring a smooth deployment.
ISRO’s Announcement on X
ISRO announced the launch on X, saying, “Liftoff Day is Here! PSLV-C59, showcasing the proven expertise of ISRO, is ready to deliver ESA’s PROBA-3 satellites into orbit. This mission, powered by NSIL with ISRO’s engineering excellence, reflects the strength of international collaboration. A proud milestone in India’s space journey and a shining example of global partnerships. Liftoff: 4th Dec 2024, 16:08 IST. Location: SDSC-SHAR, Sriharikota. Join NSIL, ISRO, and ESA as history unfolds!”
About the PSLV
The PSLV is an essential launch vehicle for ISRO, designed to carry satellites and other payloads into space. Notably, it was India’s first vehicle equipped with liquid stages. The first successful PSLV mission took place in October 1994, setting the stage for future space missions.
Launch Vehicle Details
The PSLV-C59 will feature four stages and will carry a total mass of about 320 tonnes. This robust design emphasizes the vehicle’s precision and reliability.
Precision and Collaboration
In conclusion, the PSLV-C59 mission demonstrates both ISRO‘s trusted precision and the success of international collaboration. It highlights the strength of partnerships with agencies like ESA and showcases India’s growing capabilities in space exploration.