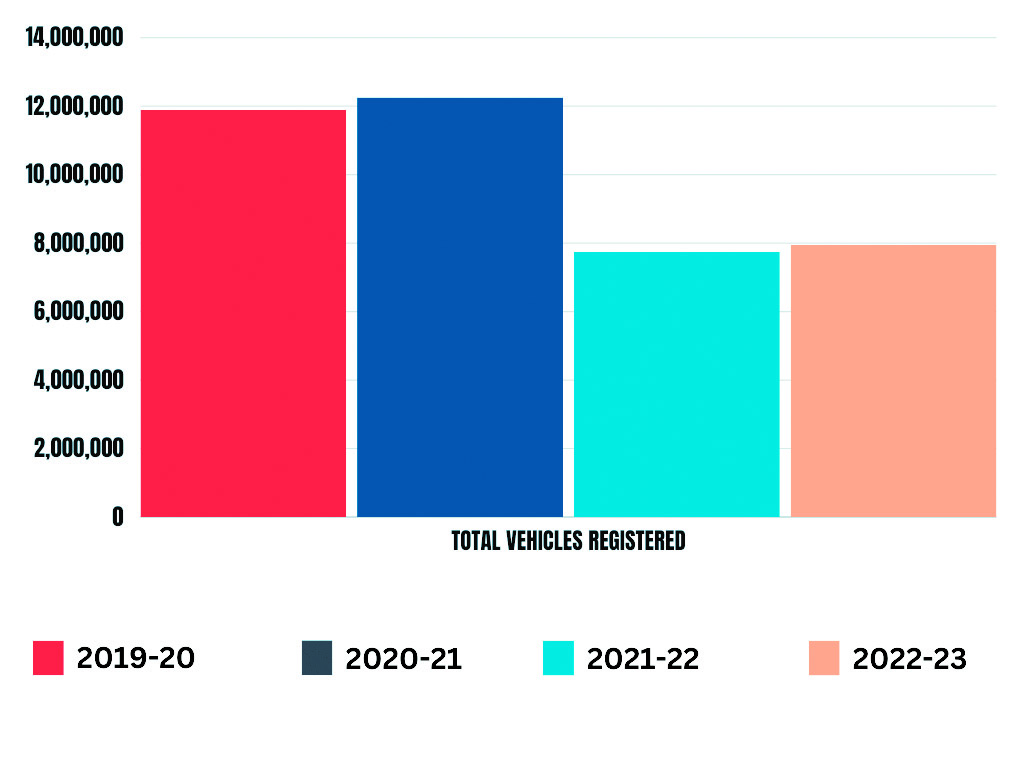
During the fiscal year 2022-23, Delhi marked a noteworthy advancement in promoting sustainable transportation, showcasing a substantial surge in the decommissioning of outdated vehicles. This proactive approach towards phasing out overage vehicles reflects the city’s commitment to fostering environmentally responsible practices and embracing a greener and more sustainable urban mobility landscape.
The increased emphasis on scrapping aged vehicles not only contributes to reducing air pollution and traffic congestion but also aligns with the broader goal of creating a cleaner and more eco-friendly urban environment for the residents of Delhi.
In adherence to directives from the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and the Supreme Court, the transport department made a significant announcement in December 2021. According to the new regulations, all diesel vehicles reaching 10 years of age and petrol vehicles reaching 15 years of age were slated for de-registration.
This strategic initiative was propelled by the overarching objective of curbing vehicular pollution in the city. By systematically de-registering older vehicles, Delhi aimed to enhance air quality, aligning with the broader vision of creating a cleaner and healthier living environment for its residents.
This decisive step underscores the commitment of the authorities to address environmental concerns and foster sustainable urban practices in the national capital.
As detailed in the Statistical Handbook-2023 unveiled by the Delhi government’s Economic and Statistics department, a remarkable milestone was achieved in the realm of sustainable transportation during the financial year 2022-23.
The data revealed a noteworthy surge in the scrapping of vehicles, reaching an impressive total of 1,40,342 units. This figure represents a significant escalation compared to the relatively modest 4,923 vehicles scrapped in the preceding fiscal year of 2021-22.
The substantial increase in the number of vehicles being retired highlights a positive trend towards environmental responsibility and aligns with the city’s endeavours to address vehicular pollution and promote sustainable practices in the transportation sector. This robust initiative underscores the commitment of Delhi to usher in a greener and more eco-friendly urban landscape.
The notable increase in vehicle scrapping, as highlighted in the Statistical Handbook-2023 released by the Delhi government’s Economic and Statistics department, is in consonance with the strategic goals outlined in the Delhi government’s Electric Vehicle Policy.
Enacted in August 2020, this policy sets ambitious targets, envisioning a 25% share of electric vehicles in the city by the year 2024. In alignment with its commitment to sustainable and eco-friendly transportation, the policy incorporates incentives for scrapping, thereby encouraging the retirement of older, more polluting vehicles.
This holistic approach not only propels the adoption of electric vehicles but also addresses environmental concerns by phasing out outdated, emission-heavy vehicles. The surge in vehicle scrapping serves as a tangible manifestation of the city’s commitment to fostering a cleaner and greener urban mobility landscape.
Despite its expiration in the previous year, the Electric Vehicle Policy has undergone multiple extensions, with the latest extension stretching its impact until March 31. The forthcoming Electric Vehicle Policy 2.0, currently in the developmental phase, suggests a continued commitment to sustainable transportation strategies in Delhi.
To address the issue of ‘end-of-life’ (ELV) vehicles, the transport department presented vehicle owners with several alternatives. Owners had the option to obtain a No Objection Certificate (NOC) and relocate their vehicle to another state.
Alternatively, they could opt to have their vehicles scrapped at government-approved scrapyards, contributing to sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
Another avenue offered was the retrofitting of vehicles with electric kits, a process managed through agencies sanctioned by the Transport Department; however, this retrofitment process is still in progress.
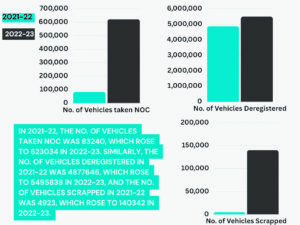
Delving into the detailed statistics provided by the handbook, a substantial surge in the deregistration of overage vehicles is evident. In the fiscal year 2022-23, a noteworthy 54,95,838 overage vehicles were deregistered, showcasing a significant increase from the 48,77,646 recorded in the preceding fiscal year of 2021-22.
This surge in deregistration aligns with the broader objectives of promoting environmentally friendly practices and reducing vehicular pollution in the national capital. The evolving landscape of vehicle management and sustainable policies demonstrates the city’s dedication to fostering a cleaner and more efficient transportation ecosystem.
Additionally, in the fiscal year 2022-23, a substantial number of vehicles, specifically 6,23,034, applied for No Objection Certificates (NOC) from the Transport Department, indicating their intent to relocate to other states and neighbouring cities such as Gurgaon, Noida, and Ghaziabad. This marks a significant increase from the 83,240 vehicles that sought NOCs in the preceding fiscal year.
The notable rise in the number of vehicles seeking relocation suggests dynamic shifts in urban mobility patterns and emphasizes the importance of regional transport dynamics in the broader context of city planning and development. The transition towards sustainable transportation in Delhi is evident in the electric bus sector. In the fiscal year 2021-22, the city had only two electric buses, both non-operational.
However, in the following fiscal year, there was a remarkable surge, with the number escalating to 300 electric buses. Among them, 202 buses are actively in operation on the city’s roads. This substantial increase not only underscores the commitment to eco-friendly public transportation but also signifies a significant leap towards reducing the carbon footprint in the national capital.
The report underscores a significant advancement in the realm of electric buses, noting a substantial escalation from merely two non-operational electric buses in 2021-22 to a commendable fleet of 300 in the subsequent fiscal year, with 202 actively traversing the city’s roads.
In tandem with this surge in electric buses, there is a noteworthy increase in the number of passengers opting for this eco-friendly mode of transportation. The figures rose from 5702.20 lakh passengers in 2021-22 to an impressive 9132.90 lakh in the fiscal year 2022-23, signifying a considerable shift towards sustainable and efficient public transit.
The data highlights a safety improvement, indicating a decline in bus accidents from 118 in the fiscal year 2021-22 to 95 in 2022-23. In the former fiscal year, fatal accidents involved 20 buses, with four in major accidents and 71 in minor accidents.
Conversely, in the subsequent fiscal year, fatal accidents decreased to 36 buses, major accidents involved 10 buses, and minor accidents comprised 72 buses. The analysis of the safety aspect reveals a positive trend, showcasing a reduction in the number of buses involved in accidents from 118 in 2021-22 to 95 in 2022-23.
Fatal accidents experienced a notable decrease from 20 to 10, while major accidents dropped from four to zero. Simultaneously, the number of minor accidents showed a slight increase from 71 to 72.
Detailed statistics also indicate that 55 cluster buses were involved in accidents during 2022-23. Among them, 29 were part of fatal incidents, 15 in major accidents, and 11 in minor ones. This underscores the ongoing necessity for sustained efforts aimed at bolstering safety measures in public transportation.
Delhi’s initiatives in sustainable transportation, exemplified by the heightened vehicle scrapping and the incorporation of electric buses, illustrate a positive transition towards a more environmentally friendly and secure urban mobility scenario.