Breaking the Vape Habit: Challenges Faced by Young Adult Users
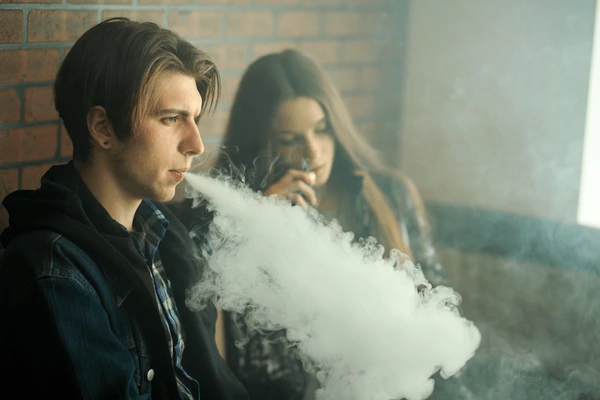
Vaping, once marketed as a safer alternative to smoking, has quickly become a popular trend, especially among young adults. Over the past decade, vaping has surged in popularity due to its perceived safety compared to traditional cigarettes, its appealing flavors, and the perception that it is a “cool” activity. However, as more research emerges, concerns about the long-term effects of vaping are intensifying. Despite the awareness of its potential health risks, many young adults continue to vape, and breaking the habit proves to be a significant challenge. This article delves into the factors that contribute to the difficulties young adults face when attempting to quit vaping, as well as the societal, psychological, and physical aspects that make this habit so difficult to break.
Vaping involves inhaling vapor produced by an electronic cigarette or similar device. These devices work by heating a liquid (often containing nicotine, flavoring, and other chemicals) to produce an aerosol, which is then inhaled by the user. While vaping is commonly believed to be a safer alternative to smoking, studies have shown that it still carries significant health risks, including lung damage, heart problems, and potential addiction to nicotine.
The allure of vaping for young adults can be attributed to several factors. The sleek, modern design of e-cigarettes, the availability of sweet and fruity flavors, and the social influence of peers make vaping particularly appealing to this demographic. Moreover, the marketing strategies by vaping companies often focus on youth culture, with advertisements that emphasize lifestyle and appeal to a sense of rebellion.
Another critical factor is the perception that vaping is less harmful than smoking. Many young adults believe that since e-cigarettes do not produce tar or smoke, they are harmless. However, emerging research has revealed that vaping can cause damage to the lungs and heart, and may also have negative long-term effects on brain development in young users. Despite this knowledge, the popularity of vaping continues to rise, particularly among teenagers and young adults.
Quitting any addictive behavior can be challenging, but breaking the vaping habit is especially difficult for young adults. Several factors contribute to the struggle of quitting, including addiction to nicotine, social pressures, and the emotional and psychological connections formed with the habit.
Nicotine is a powerful addictive substance, and it is the primary reason why many young adults find it difficult to quit vaping. When nicotine is inhaled, it enters the bloodstream quickly, reaching the brain within seconds. This rapid absorption causes a release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward, leading to feelings of euphoria. Over time, the brain becomes dependent on nicotine to trigger this pleasure response, creating a cycle of addiction.
For young adults who started vaping at an early age, their brains are still developing, making them more vulnerable to nicotine addiction. As they continue to vape, their bodies and brains become accustomed to the substance, leading to increased tolerance. This means that users need higher doses of nicotine to achieve the same effect, making it even harder to quit.
The withdrawal symptoms from nicotine addiction can be intense and include irritability, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, cravings, and even physical symptoms like headaches and nausea. These symptoms can make the process of quitting uncomfortable, leading many young adults to relapse and return to vaping.
Beyond the physical addiction, there is also a psychological and emotional attachment to the act of vaping. Many young adults use vaping as a way to cope with stress, anxiety, or other emotional issues. Vaping can provide a temporary escape, a way to manage difficult feelings or social pressures, and for some, it becomes a way to feel included in social situations.
For young adults who use vaping as a coping mechanism, quitting can feel like giving up an emotional support system. The sense of relief or comfort that comes from vaping can make it harder to break free from the habit, as users may feel overwhelmed without that outlet for emotional release.
Vaping can also be a form of social bonding for young adults. Many users vape together in groups, sharing their experiences, and forming friendships based on their mutual habit. This social aspect of vaping can create a strong sense of community and belonging, making it more difficult for individuals to quit. Peer pressure, whether direct or indirect, can make young adults feel like they are missing out on social connections if they quit vaping.
Another significant challenge in breaking the vape habit is the influence of marketing and social media. Vaping companies have been known to target young people through advertisements that feature influencers, appealing aesthetics, and catchy slogans. These advertisements often present vaping as a fun and harmless activity, further reinforcing the idea that it is a safe and trendy habit.
Social media platforms are flooded with influencers and celebrities who promote vaping, often without disclosing the potential health risks involved. The normalization of vaping in these digital spaces can make it difficult for young adults to see it as anything other than a socially acceptable and enjoyable activity. When these influencers show vaping as part of their daily routine, it makes quitting feel like a solitary and unappealing choice for many young adults.
Additionally, social media can also be a platform where vaping culture is glorified. Hashtags such as #vape, #vapingcommunity, and #vapejuice are commonly used by young people to share their experiences and connect with others who vape. This widespread presence of vaping on social media contributes to the normalization of the habit, making it even harder to break free from its grip.
While there is a growing awareness of the dangers of vaping, many young adults lack the resources and support necessary to help them quit. In contrast to smoking, which has been widely publicized as a dangerous habit with well-established quitting methods, vaping is still a relatively new issue, and many healthcare providers and educators are not equipped with the knowledge or resources to address it effectively.
Moreover, some young adults feel embarrassed or ashamed to seek help for quitting vaping. The stigma around addiction and the feeling of personal failure can prevent individuals from reaching out to support groups, counselors, or medical professionals. Without proper guidance, young adults may feel overwhelmed by the process of quitting, unsure of where to turn for help.
There is also the challenge of finding effective cessation tools. While nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), such as nicotine gum, patches, and lozenges, has been proven to help people quit smoking, there is limited research on the effectiveness of these tools for vaping. Additionally, other strategies, such as behavioral therapy, may not be tailored specifically for young adults who vape. This lack of targeted cessation programs can leave many young people struggling to find the right solution.
Despite these challenges, breaking the vape habit is not impossible. Several strategies can help young adults overcome their addiction to vaping, and with the right support, many individuals have successfully quit.
Breaking the vape habit is a complex and challenging process for young adults. The combination of nicotine addiction, psychological attachment, social pressures, and lack of resources makes it difficult for individuals to quit. However, with the right support, education, and strategies in place, it is possible to overcome the addiction and improve health. As awareness of the risks of vaping continues to grow, it is crucial that young adults have access to the information and resources they need to make informed decisions and ultimately break free from the vape habit.