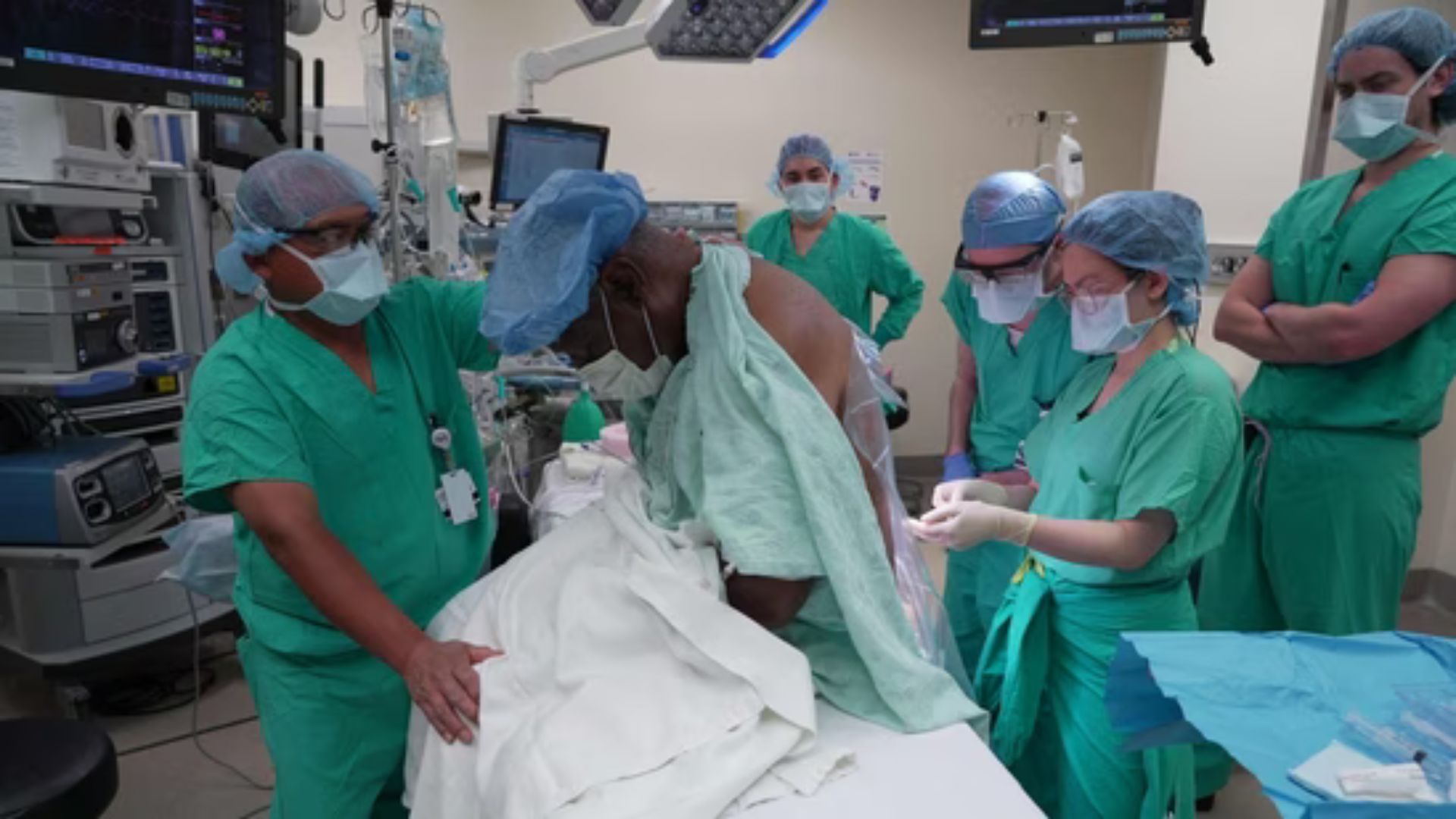
In the evolving landscape of surgical medicine, awake kidney transplants are emerging as a potential game-changer. Traditionally, kidney transplants have been performed under general anesthesia, but a new approach where patients remain conscious but sedated is gaining traction. Could this method become the new standard in surgery? Here’s an in-depth look at the possibilities and challenges of awake kidney transplants.
What Are Awake Kidney Transplants?
Awake kidney transplants involve performing the surgery while the patient is awake but sedated with local or regional anesthesia. This technique contrasts with the conventional approach, where patients are fully anesthetized and unconscious throughout the procedure.
Benefits of Awake Kidney Transplants
- Faster Recovery: One of the most significant advantages of awake kidney transplants is the potential for quicker recovery. Without the lingering effects of general anesthesia, patients often experience reduced postoperative confusion and a faster return to normal activities. This can lead to shorter hospital stays and a more rapid overall recovery.
- Reduced Surgical Risks: General anesthesia carries inherent risks, particularly for patients with pre-existing health conditions. By using local or regional anesthesia, awake kidney transplants mitigate these risks, making the procedure safer for high-risk individuals who might otherwise face complications.
- Cost Savings: General anesthesia and its associated monitoring can be expensive. By eliminating the need for these additional resources, awake kidney transplants could lower overall surgical costs. This reduction in expenses might make the procedure more accessible to a broader range of patients.
Challenges and Considerations
- Patient Comfort: Despite being sedated, the prospect of being awake during surgery can be daunting for many patients. Ensuring patient comfort and managing anxiety are crucial aspects of the procedure. Advanced sedation techniques and psychological support are essential to address these concerns.
- Technical and Skill Requirements: The success of awake kidney transplants depends heavily on the precision of the surgical team and the technology employed. Specialized skills and advanced techniques are necessary to perform the surgery effectively while the patient remains conscious. Ongoing training and technological advancements will be critical in making this approach widely feasible.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Research is still ongoing to assess the long-term outcomes of awake kidney transplant compared to traditional methods. Comprehensive studies are needed to determine whether this approach offers similar or improved results in terms of graft survival, patient health, and overall success rates.
Looking Ahead
Awake kidney transplant represent an exciting development in surgical medicine, offering potential benefits such as faster recovery, reduced risks, and lower costs. However, their widespread adoption will depend on continued research, successful implementation, and addressing the challenges associated with patient comfort and technical execution.
As the medical community explores this innovative approach, awake kidney transplant could indeed become a new standard in kidney transplant surgery, offering a promising alternative to traditional methods. For now, patients and healthcare providers alike should stay informed and consider the evolving landscape of surgical options as they navigate the future of kidney transplantation.