Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated levels of blood sugar (glucose) in the body. This occurs when the body either cannot produce enough insulin (a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is crucial for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, where it is used as an energy source.
There are several types of diabetes, with the most common being Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes is another type that can occur during pregnancy.
The lifestyle between creation and deterioration has severely fragmented human life. Due to lifestyle changes, the abdomen is expanding, and life is diminishing, with everyone living either with the past or with dreams of the future. Some are deteriorating in the storm of the past, and some are facing trouble in today’s whirlwind, while tomorrow is approaching
Currently, due to excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates (flour, white rice, and sugar), rest, and stress, insulin resistance is steadily increasing, leading to a declining quality of life.
1. Type 1 Diabetes:
• Cause: It is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
• Onset: Typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence.
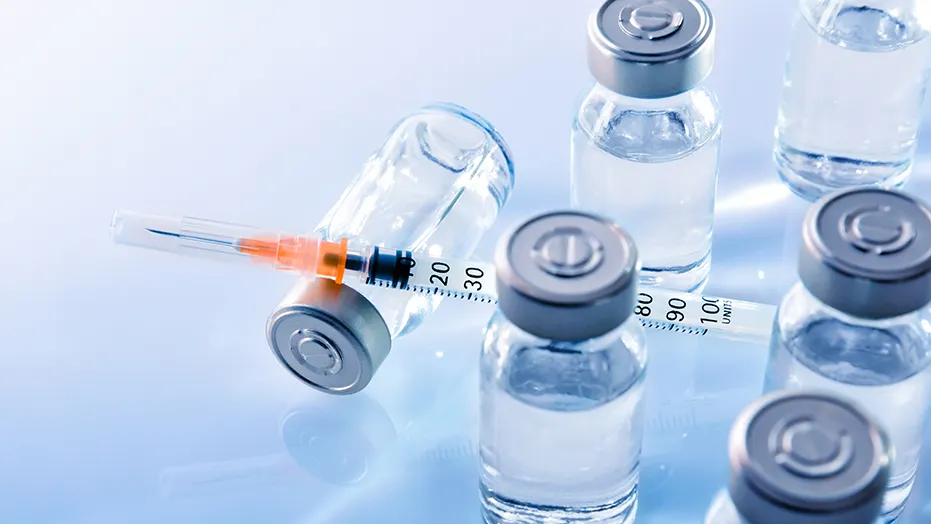
• Insulin Dependency: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin through injections or an insulin pump.
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
• Cause: Results from a combination of insulin resistance (where cells do not respond properly to insulin) and relative insulin deficiency.
• Onset: Commonly occurs in adulthood, but increasingly diagnosed in children and adolescents due to lifestyle factors.
• Management: Diet, exercise, oral medications, and sometimes insulin injections are used to manage Type 2 diabetes.
3. Gestational Diabetes:
• Occurrence: Develops during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased needs, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
• Risk: Increases the risk of Type 2 diabetes for both the mother and the child later in life.
• Management: Dietary changes, exercise, and, in some cases, medication are used to control blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
4. Other Types:
• Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diabetes diagnosis. It is a warning sign of potential future diabetes.
• Monogenic Diabetes: Caused by a mutation in a single gene, leading to abnormalities in insulin production.
Symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes and the individual. Here are common symptoms associated with diabetes:
Frequent Urination (Polyuria): Excessive thirst and increased urine production are common signs of diabetes. The body tries to eliminate excess sugar through urine.
Increased Thirst (Polydipsia): Dehydration caused by frequent urination can lead to increased thirst.
Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite increased appetite, individuals with diabetes may experience weight loss due to the body breaking down muscle and fat for energy when it cannot use glucose effectively.
Fatigue: Feeling tired and lacking energy is a common symptom, often related to the body’s inability to efficiently convert glucose into energy.
Blurred Vision: High levels of blood sugar can affect the lenses in the eyes, causing blurred vision.
Slow Wound Healing: Diabetes can impair the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow recovery from cuts, bruises, or infections.
Frequent Infections: Individuals with diabetes may be more prone to infections, especially in the skin, urinary tract, and gums.
Tingling or Numbness: Nerve damage (neuropathy) due to uncontrolled diabetes can result in tingling or numbness, especially in the extremities.
Dry Skin and Itching: Diabetes can lead to skin problems, including dryness and itching.
Increased Hunger (Polyphagia): Despite eating, individuals with diabetes may still feel hungry due to the body’s inability to use glucose effectively.
Managing diabetes with lifestyle involves making healthy choices in terms of diet, physical activity, stress management, and overall well-being. Here are some key lifestyle strategies for managing diabetes:
Healthy Eating:
• Focus on a well-balanced diet with a variety of nutrient-rich foods.
• Choose complex carbohydrates (whole grains, vegetables, fruits) over refined carbohydrates.
• Monitor portion sizes to help regulate blood sugar levels.
• Include lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fiber in your meals.
Regular Physical Activity:
• Engage in regular exercise, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
• Include both aerobic exercises (walking, jogging, swimming) and strength training exercises.
• Consult with your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise routine.
Weight Management:
• Maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can contribute to insulin resistance.
• Focus on gradual, sustainable weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise.
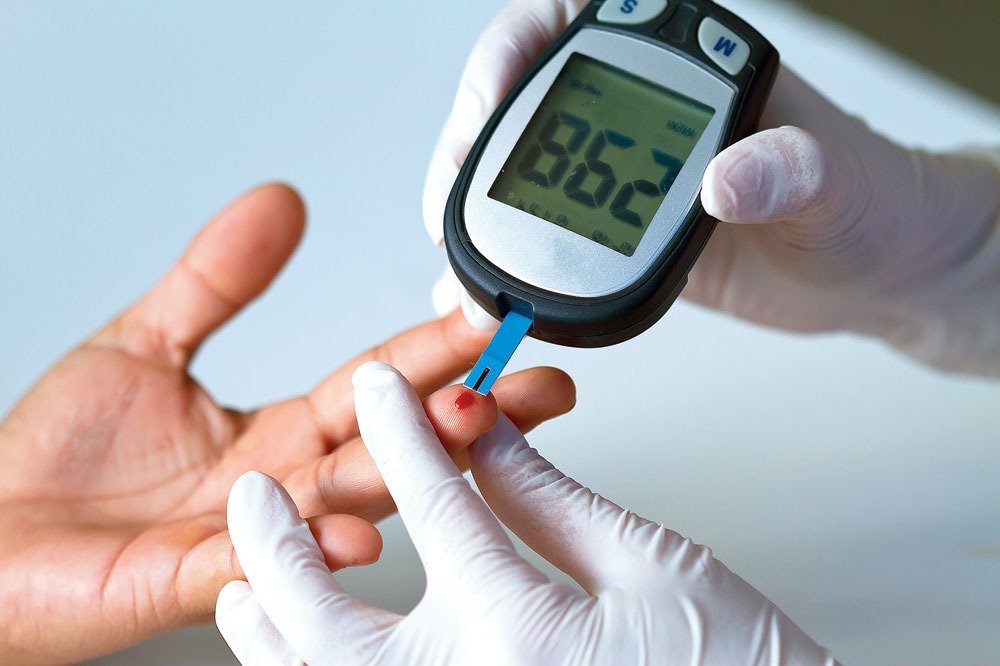
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring:
• Monitor blood sugar levels regularly to track the effects of lifestyle changes.
• Keep a log of your readings and share them with your healthcare team during check-ups.
Stress Management:
• Practice stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or mindfulness.
• Identify and address sources of stress in your life.
Adequate Sleep:
• Ensure you get enough quality sleep each night.
• Lack of sleep can affect insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
• If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation and always with food.
• Monitor blood sugar levels to understand how alcohol affects you individually.
Quit Smoking:
• If you smoke, consider quitting, as smoking can contribute to complications related to diabetes.
• Seek support from healthcare professionals or smoking cessation programs.
Regular Medical Check-ups:
• Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare team to monitor overall health and receive guidance on diabetes management.
Medication Adherence:
• If prescribed medication, take it as directed by your healthcare provider.
• Discuss any concerns or side effects with your healthcare team.
It’s crucial to individualize your diabetes management plan with the guidance of healthcare professionals who can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and circumstances. Regular communication with your healthcare team is essential for adjusting your lifestyle plan as needed and optimizing diabetes management. In conclusion, effective diabetes management is a multifaceted approach that requires a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication (if necessary), regular monitoring, and ongoing communication with healthcare professionals. The goal of diabetes management is to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range to prevent complications and improve overall well-being.
Dr Sunil Dhand is Endocrinology consultant.