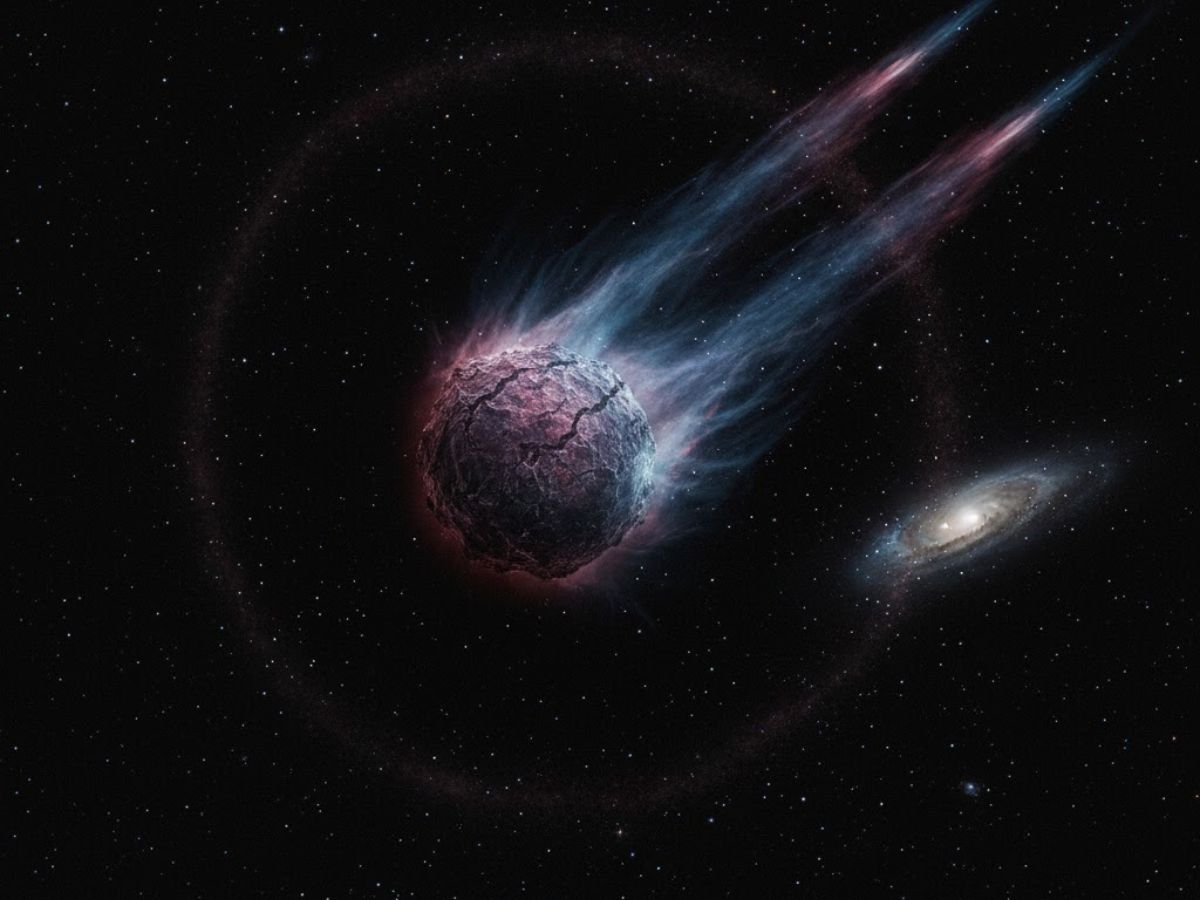
The interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is believed to be between 8 and 14 billion years old, far older than our 4.6-billion-year-old solar system. This extreme age means the icy object could be a relic from a star that no longer exists, according to scientists studying its path and composition.
Associate Professor Michele Bannister of the University of Canterbury (UC), who has studied the comet since its July 2025 discovery, calls it a “once in a lifetime opportunity.” She says such interstellar objects offer a direct peek into the building blocks of planet formation elsewhere in the Milky Way galaxy.
What Is the Significance of 3I/ATLAS’s Age?
The comet’s estimated age of 8 to 14 billion years makes it a primordial messenger. “This comet is a calling card from the past, and we only have a few hundred days to try and interpret what it’s telling us,” Bannister told Astrobiology. According to its ancient beginnings, the comet may have originated around a star in the early galaxy that has since died, leaving it to roam interstellar space for generations.
What Clues Does the Comet Provide?
Interstellar objects like 3I/ATLAS are unique samples from other star systems. “They’re giving us clues, because they’re made up of the building blocks of planet formation elsewhere in the galaxy,” Bannister said. “They’re telling us about a star that’s so ancient it might not even exist anymore.” The UC team, with Professor Chris Lintott at Oxford, first theorized its great age based on its velocity shortly after discovery.
How Are Scientists Studying Its Composition?
Bannister’s team uses a theoretical model called the Ōtautahi-Oxford model to analyze interstellar objects. They have studied 3I/ATLAS’s coma and its two tails—one tail and one anti-tail pointing toward the Sun. The visible tails are made of ice and dust grains that reflect sunlight, leading Bannister to call the object “a dusty wee snowball.”
What Did Its Chemical Makeup Reveal?
The comet’s composition speaks volumes about its home environment. Bannister reported that as it entered our skies, they observed an “unusually rich atomic nickel and iron emission.” This particular chemical signature offers forensic proof of the materials and conditions that existed in its parent star system billions of years ago.
FAQs: Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS
Q: How old is comet 3I/ATLAS?
A: Scientists estimate it is between 8 and 14 billion years old, much older than our 4.6-billion-year-old solar system.
Q: What does its age imply?
A: Its extreme age suggests it could have originated around a star so ancient that the star may no longer exist.
Q: Who is studying the comet?
A: A team led by Associate Professor Michele Bannister at the University of Canterbury, in collaboration with Professor Chris Lintott at the University of Oxford.
Q: What is unusual about its composition?
A: Researchers detected an unusually rich signature of atomic nickel and iron as the comet entered our solar system.
Also Read: Who is Jumaane Williams, NYC’s Public Advocate? Career, Wife & Progressive Agenda