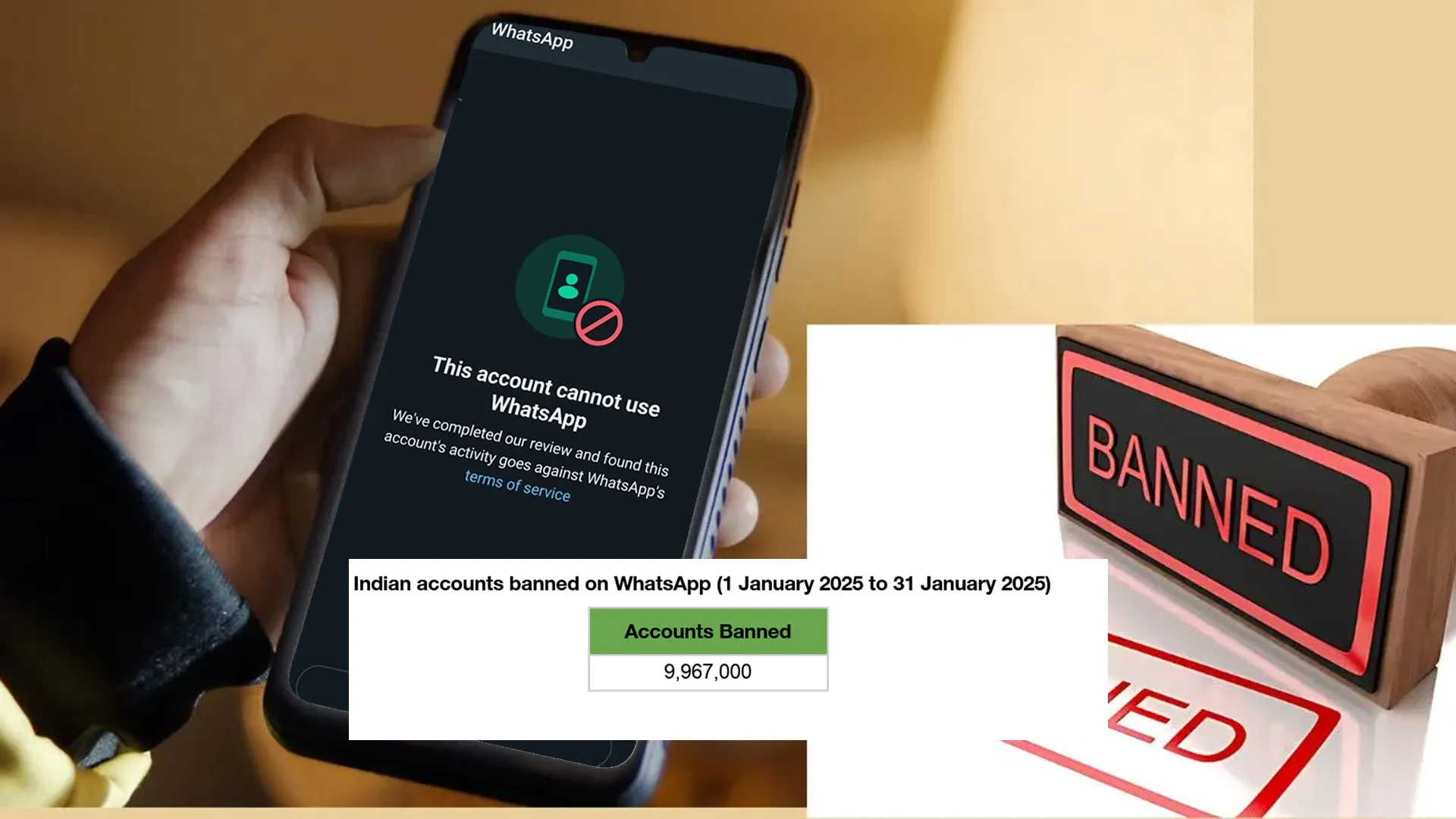
Cybercrime incidents linked to social media and online platforms have nearly tripled in the past five years, according to data from the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) presented in the Lok Sabha. This rapid increase highlights the growing challenges of digital safety in India.
The total number of reported cases jumped from 56,283 in 2020 to 1,56,938 in 2024. The National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP) recorded 72,301 cases in 2021, reflecting a 28.5% rise from the previous year. In 2022, cases surged by 82.1%, reaching 1,31,634. The numbers continued to rise, hitting 1,41,264 in 2023 and 1,56,938 in 2024, an 11.1% increase from the previous year.
Social Media Crimes See a Drastic Rise
Cybercrimes involving social media platforms have seen an alarming increase. Cases of identity theft, fake profiles, and online fraud have skyrocketed, making digital security a major concern.
- Fake or Impersonating Profiles: Reports grew from 12,310 in 2020 to 39,846 in 2024, marking a 224% jump.
- Profile Hacking & Identity Theft: Cases surged from 10,419 in 2020 to 38,295 in 2024, reflecting a 267% rise.
- Cyber Bullying, Stalking, and Sexting: These crimes more than tripled, increasing from 11,641 cases in 2020 to 39,077 in 2024.
- Cheating by Impersonation: Incidents doubled, rising from 9,808 in 2020 to 19,989 in 2024.
- Online Job Fraud: Cases increased from 4,973 in 2020 to 10,461 in 2024, indicating a rise in employment-related scams.
Government Strengthens Cybersecurity Measures
To combat this growing threat, the government has intensified its cybersecurity efforts through the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C). Authorities have taken several steps to enhance digital security and law enforcement capabilities.
- AI-Driven Monitoring: The government has deployed advanced AI systems to track and prevent cybercrimes more efficiently.
- Enhanced Law Enforcement Tools: Authorities now use sophisticated tracking systems to identify cybercriminals quickly.
- Cyber Forensic Labs Across India: The government has set up forensic laboratories in 33 states and union territories to support digital investigations.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: The government has launched initiatives to educate citizens about online threats and safe internet practices.
Legal Actions to Regulate Cybercrime
The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) now officially oversees cybercrime regulation under the Information Technology Act, 2000. The MHA announced this on March 13, 2024, granting I4C the authority to monitor and take action against unlawful online activities.
With cyber threats increasing rapidly, the government is taking proactive steps to strengthen digital security. By improving law enforcement, enhancing public awareness, and using advanced technology, India aims to tackle the growing menace of cybercrime effectively.