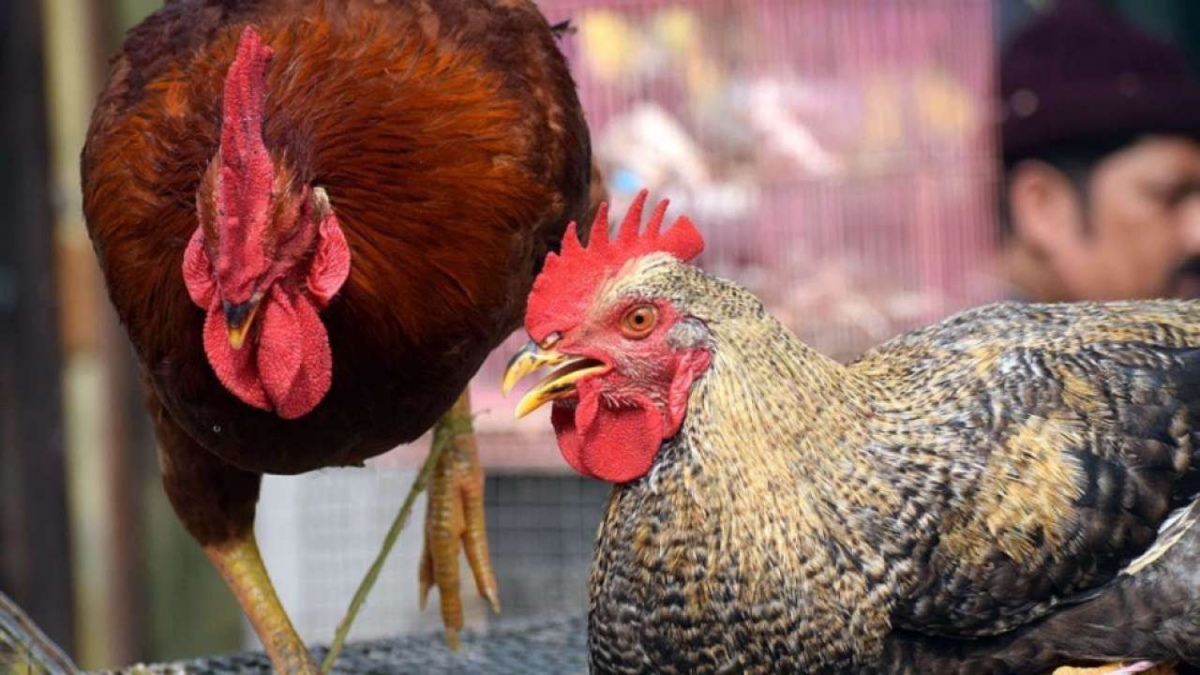
Russia has confirmed the first case of human infection with the avian influenza A (H5N8) virus in the world, a Russian sanitary official announced on Saturday.
Scientists have isolated the genetic material of this bird flu virus in seven workers of a poultry farm in south Russia, where an outbreak among fowls was reported in December, said Anna Popova, head of the country’s consumer rights and human well-being watchdog Rospotrebnadzor, say reporters.
Outbreaks of the H5N8 strain have been reported in India, Russia, Europe, China, Middle East and North Africa in recent months but so far only in poultry.
Russia reported the case of human infection to the WHO “several days ago, just as we became absolutely certain of our results,” Popova said on Rossiya 24 state TV. There was no sign yet of transmission between humans, she added.
Seven workers at a poultry plant in Russia’s south had been infected with the H5N8 strain in an outbreak at the plant in December, Popova said, adding that the individuals involved felt fine now.
“This situation did not develop further,” she said.
In an email WHO’s European arm said that it had been notified by Russia about a case of human infection with H5N8 and acknowledged this would if confirmed be the first time the strain had infected people.
“Preliminary information indicates that the reported cases were workers exposed to bird flocks,” the email said. “They were asymptomatic and no onward human to human transmission was reported. We are in discussion with national authorities to gather more information and assess the public health impact of this event,” it added.
The majority of human bird flu infections have been associated with direct contact with infected live or dead poultry, though properly cooked food is considered to be safe.
Bird flu outbreaks often prompt poultry plants to kill their birds to prevent the virus from spreading, and avoid importing countries having to impose trade restrictions.
The vast majority of cases are spread by migrating wild birds, so producing countries tend to keep their poultry indoors or protected from contact with wildlife.
Siberia’s Vector Institute said on Saturday it would start developing human tests and a vaccine against H5N8, RIA news agency reported.
With agency inputs
Bird flu outbreaks often prompt poultry plants to kill their birds to prevent the virus from spreading, and avoid importing countries having to impose trade restrictions. The majority of human bird flu infections have been associated with direct contact with infected live or dead poultry, though properly cooked food is considered to be safe.