ABSTRACT
The article gives an analytical information about rising cyberattacks and cybercrimes in India. there is data transferring or acquiring personal information of users by hacking, frauds or unknown internet viruses. During this catastrophic time, people are vulnerable to internet use, and resultantly became victims of cybercrimes. The article highlights the facts of the cybercrime in lockdown as well as legal aspects of such crimes. further, there are some suggestive defences for addressing the cybercrimes observed in foreign laws and some analytical observation of experts to reduce cybercrimes. In the end, it concludes on the importance of privacy as the fundamental right of the citizens of India and explains the need for such suggestive alternative laws in India to be recommended by government and administrative bodies.
INTRODUCTION
During the pandemic period, as the world is suffering through a major health crisis, many other dark elements with atrociousness and treacherousness have raised since the lockdown has started. As people were in their respective homes and following the rules of the government, the medium to get used to this lifestyle was the internet browsing and social media surfing, which turns out to be very dangerous because of data transferring or acquiring personal information of anyone by hacking, frauds or unknown internet viruses. It has been discovered that such viruses or frauds are a medium to get access to personal information of the user.
In the catastrophic time of the pandemic, people are vulnerable to internet use, and therefore became victims of cybercrimes. Internet is also a necessary for many corporate and government office employees who are working from home in the lockdown. Cases of data breach through unsecured apps for official meetings in the lockdown is being a major concern, zoom app has been detected as a part of mediums to cybercrimes. It was observed that hackers were able to get access to the meeting IDs and the passwords during the online lectures or other official meetings, inappropriate content used to came across, and no such firewall and barrier can protect from hacking as it is seen that perpetrators are more advanced and more equipped than protectors, which leads to bring the justice for the online users as a Gordian knot.
The 21st century’s advancement in the science and data technology has been seen as a more of a sin in disguise. America after having world class internet technology for data protection cannot even anticipate the scandal like Cambridge Analytica can take place, the Cambridge Analytica scandal which shook the world for internet security and a big alert for social media security. India is not even close to the advancements of technology which America has, In India, internet security is not taken as seriously, which has resulted in the rise to cybercrimes during the pandemic. Looking to the history of cyber threat reports in India, In the cyber threat report of 2019, around 65% of firms face cyber attack in 2019, As per the cyber security reports of 2018 by CISCO, it was found that around 53% of the cyber attacks caused the financial loss of 3.5cr rupees.
As per the report by India Today it was found that Chennai has experienced major cyber attacks with a stat of around 48% in the 2019. It’s the wake-up call to have a major concern for strengthening internet technology, laws of internet technology and to have an extraordinary array of cyber security in the country.
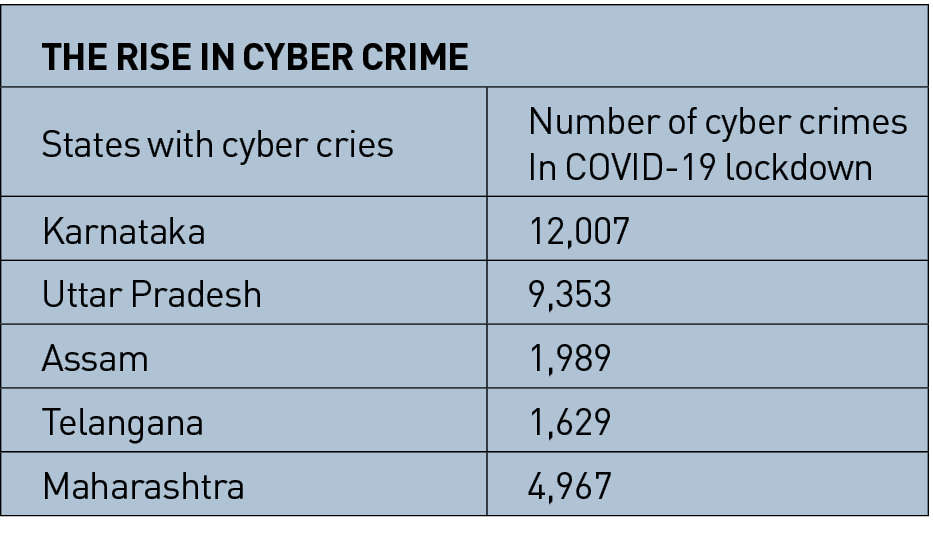
The I.T capital of India, Hyderabad has reported 1,300 cases under information technology Act, 2019 in the year 2020, the city has 70% of increase in cybercrimes. Similarly, Bangalore and other I.T. hub of India has become the highest reported cybercrime city, over 10,555 cases in 2019 that has raised in the lockdown simultaneously, making Karnataka the highest number of cybercrimes. This raises question over how safe India on internet website and cyber space is, as the I.T hubs of the country are the most affected by cybercrimes. In Maharashtra there is 40% rise in cyber crimes compared to last year, crimes related to fraud payment and banking have increased in lockdown. Uttar Pradesh and Assam have comparatively lesser in number of cybercrimes than other states, this is probably because of less use of internet and low digitalization in the sates. In the year 2019, 4,4546 cases of cybercrimes were registered as compared to 28,248 in 2018 as per National Crime Record Bureau data (NCRB). The rise of cybercrimes has already started since last year, The COVID-19 lockdown that started since early 2020 has made a repulsive effect on cybercrimes.
Already More than 550 million Indians that have connected to the Internet in recent years, fueled by rural growth. But the rapid proliferation of Internet users has also left the country’s public and private sectors vulnerable to a cyber attack during the lockdown because most of the work is being done online, it gave an open invitation to cyberattacks moreover the Indian cybersecurity is weak to protect the internet users. There is a dramatic rise in cybercrimes across the country, cyberattacks have soared 86% in the four weeks between March and April, a recent Reuters report quoting Indian Home Ministry officials and detailing fake offers from telecom and streaming services like Netflix Inc, offering discounted services in the lockdown.
According to city crime records bureau data Bangalore, March and April together had 1,308 cybercrime cases with a jump in bank fraud and scams in such cases people impersonating government officials to trick the victims. The spike in cybercrimes and attacks has targeted general citizen’s wallets and personal data given the sharp increase in the percentage of Indian corporate workforce. The online corporate workers and digital payment users are the easy targets of cyberattacks. India’s National Cyber Security Coordinator (NCSC) reported that cybercriminals had launched thousands of fraud portals related to the coronavirus. These sites have tempted many Indians to contribute to the fight against COVID-19 into making donations. The online users and digital payment workers are the victims of cyberattacks in the lockdown.
STRENGTHENING INDIA’S CYBER DEFENCES
To construct secure cyberspace the defence mechanism against cybercrimes must be created, to make better user-friendly cyberspace, for this, India needs to strengthen cyber defence. Following are the key points:
STRINGENT DATA PROTECTION LAWS
It is a dire need to have strict data protection laws in India, as the right to privacy is a fundamental right of every person guaranteed by the constitution of India, it is important to have strict regulations that protect the privacy of persons despite the existing circumstances. In the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”) data is secured by effective regulation on personal data of users, this has reduced the threat to privacy. Therefore, after ensuring similar aims of such laws the application of artificial intelligence aimed for Covid-19 should be structured.
DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT
Any parties that act as data processors on their behalf of the data controllers must also sign a data processing agreement. As per Article 28 of the GDPR, rights and obligations of each party regarding the protection of personal data of their users are a present legally binding contract which lays down the data processing agreement to make transparency visible. Data Protection evaluation: To make the software more secured before being in the hands of the user a data protection impact assessment must be conducted by the companies offering artificial intelligence and software solutions on devices by testing them on various levels before launching them. This would help to prevent a threat to the users and making a user-friendly mechanism. The governmental websites need to have much strong data protection evaluation to protect the official data online.
USER-FRIENDLY MECHANISM
There is a need of more user-friendly machine learning tools to make the users understand and feel safe while browsing on internet. Most of the users are unknown of the internet websites and threats, this illiteracy of the internet users in India makes a victim of cybercrimes. The head of a Mumbai-based law firm of Mulla & Mulla & Craigie Blunt & Caroe, Purnima Thacker says, to reduce cybercrime risk for private companies and individuals a user-friendly cyber policy along with impactful and applicable security system, that includes training users, system analyses and quick response and assistance where a user helped in using the secure network.
Spreading awareness: The awareness and understanding of cybersecurity in this country are also one of the major concern, as people are more driven and focused towards the innovation rather its proper ways for usage. As about installing any application or any software most of the people don’t bother to check the veracity of that software or the true source of the application, even while installation people are so complacent about it regarding unknown sources and application security permission. Several improvements can be made, spreading of awareness has to come in every individual level regarding the usage and do’s and don’t of Internet technology, Children in schools and colleges should be taught about the netiquette. Parents should also need to understand their responsibilities for guiding the children about the Internet technology and also provide an open and free environment for the child to discuss if the child is facing any difficulties or atrocities in the online medium as in the pandemic, children are very much dependent on the internet as they are being educated through online medium.
SAFETY MEASURES TO BE TAKEN IN CONSIDERATION
The user should check the authenticity of the website while downloading anything from a website. There are various tools available online which checks the authenticity of websites, other than that, a person can also verify if the website has spelling mistakes or grammatical errors, dysfunctional elements and broken links.
The user must use effective and reliable antivirus for mobile and desktop. The users must change the passwords timely to protect any unknown interference. User should check the reviews and mentions on the other website as a legitimate website has reviews and mentions, A website with there is no presence of any review or mentions so it can be a sign of fake website or the website may be new. Users should check for the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificates, a website with SSL certificate means that whatever the data you provide to the website will directly reach to the site without any interference of any 3rd party, website description in detail, for example, the link may be HTTP = Bad, HTTPS = Good.
in https://, the ‘S’ stands for ‘secure’. It indicates that the website uses encryption to transfer data and provides protection from the hacker. The user must refrain from accessing anonymous Emails with attachments while sending any personal information through emails do not share any passwords.
Avoid suspicious emails that come with a sense of panic, do not have a blind trust on any links given in any mail or other medium. User should also have a check on the contents of the website, many fake websites don’t have quality and true content, most of the time it is copied, plagiarized and cloned from other sites with blur images. Whereas, a legitimate website comes with quality and distinctive content with clearly and explicitly stated details and good English.
The Emails that identify by W.H.O or any other organizations contain lotteries or offer prices, certificates on the email are mostly fake IDs to hack the data. The users must not put any information about Debit or credit cards on a website unless necessary and crosschecked. Also, a user should look for their refunds and privacy policy if the website looks as an Ecommerce portal. The user must check the terms and conditions of every website before agreeing to any terms before accessing the website. The website must not be given excessive access to any of the settings of the device, this can lead to data extraction.
CONCLUSION
The Indian cybersecurity system is poor to protect the internet users from cyberattacks even before COVID- 19 lockdown.
Due to improper security system of internet transaction and data sharing, normal people are the victims of financial and important informational losses. This issue of cyber-crimes rises more in the COVID-19 lockdown period because of two reasons, firstly because people are made to work from home through different applications and software, which are contributing factors as this lowers the security of their system. Secondly, during the time of lockdown many people have lost their jobs, economic security, and source of income this made the rise in crime in society, as there is a low possibility of going out of homes the internet became a new medium for criminals to exploit and explore, making internet browsing unsafe for the general internet user in the lockdown Different kinds of roots are used to extract information from the user for personal benefits such as banking scams, debit cards, credit card frauds, social media scams etc. The cybercriminals are using fake IDs of the renowned organization to send emails for personal benefits.
This is a serious issue of the time because of a breach of private information that is under Art 21 of the constitution of Indian as fundamental right and offence under Sec.72 of information technology, Act 2000 for breach of privacy. These sites have tempted many Indians to contribute to the fight against COVID-19 into making donations. These Fake sites are quite sophisticatedly structured, indistinguishable from other websites. The ‘PM CARES’ coronavirus fund created by the P.M.O a lot of fake versions of the site have emerged and have successfully solicited thousands of dollars from unsuspecting individuals, Indian home ministry officials said that more than 8,000 complaints have been received from Indians, home and abroad. The cybercriminals have left no stone unturned to exploit the vulnerable user by extracting their information for personal gains.
To avoid cybercrimes the Indian government should support information sharing mechanisms, build attribution capability, and strengthen the coordination of vulnerability disclosure processes, make transparency in software and other website portals and userfriendly mechanisms, these could be the steps that can be taken to better protect the country from the attacks of ongoing cyber-attacks.























