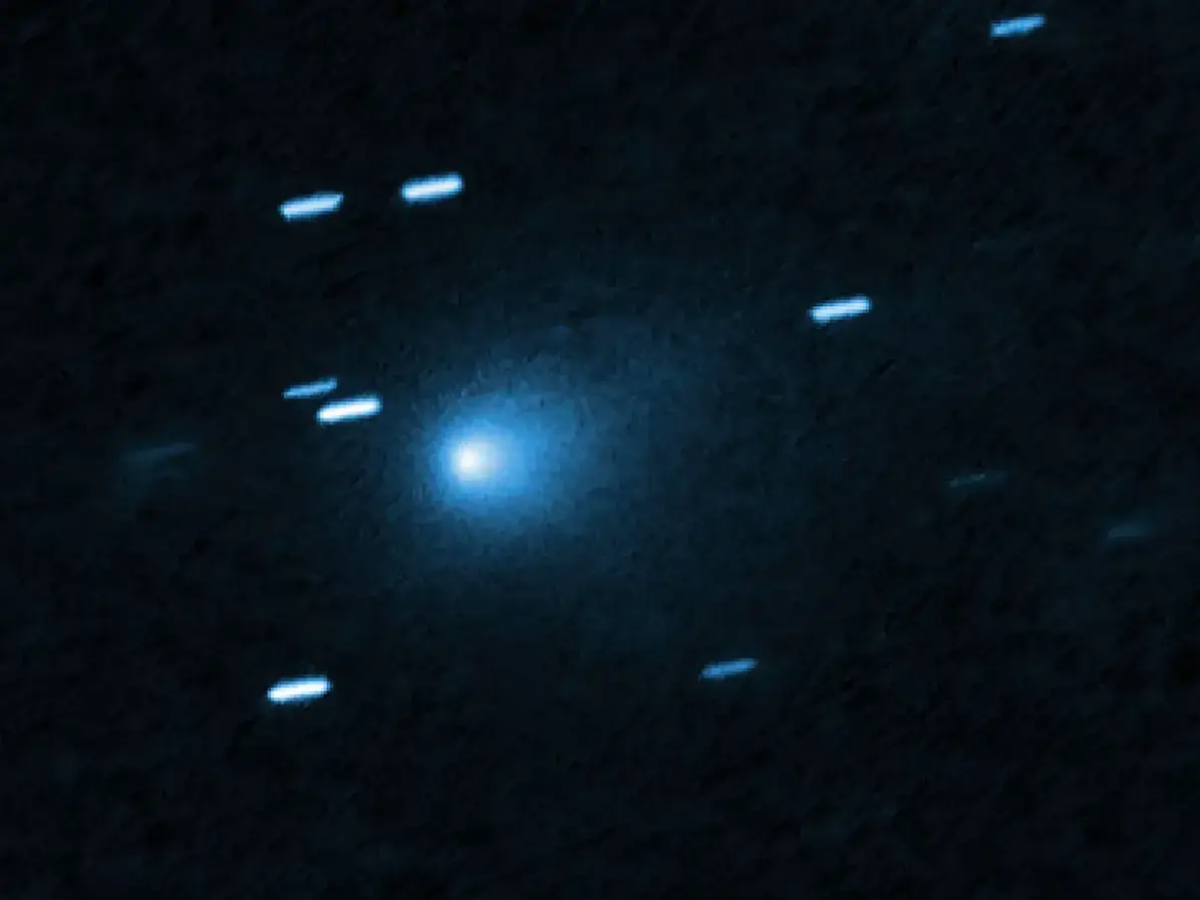
Astronomers around the world have pointed their telescopes at Comet 3I/ATLAS, the mysterious visitor from beyond our solar system. What’s special about this celestial visitor is that it’s not from our Sun’s backyard, its origin is traceable to some other star system.
Scientists believe that studying its composition could yield the first concrete evidence of interstellar ices and provide a clue about conditions around distant suns. The comet’s chemical makeup, including rare isotopic ratios, might help researchers understand how materials key for life might move between stars.
Hubble Captures a Spectacular Transformation
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has provided spectacular images of 3I/ATLAS as it draws closer toward the Sun. The pictures show how the comet’s icy core breaks apart, releasing clouds of dust and vapor that trail behind it as a glowing tail.
According to NASA scientists, the now visibly bright but steadily dimming comet is one indication of it losing mass as solar heat vaporizes its frozen layers. Such a phenomenon offers a real-time look at how interstellar objects behave when exposed to our Sun’s energy.
ALSO READ: Who is Kruti Patel Goyal? Etsy’s New CEO, Joining the League of Indian-Origin Tech Leaders | Net Worth
Webb Telescope Adds a Chemical Dimension
The James Webb Space Telescope has added a vital piece to the puzzle its instruments detected water vapor, carbon dioxide and organic compounds in the comet’s surrounding halo, or coma.
These findings suggest 3I/ATLAS shares volatile components with comets born within our own solar system but subtle differences in its chemical fingerprint could yet imply that it formed under entirely different stellar conditions-perhaps around a younger or cooler star.
A Global Effort to Track an Alien Wanderer
From the Indian Astronomical Observatory in Ladakh to observatories in Chile and Europe, telescopes across continents are tracking 3I/ATLAS in real time. Data from various wavelengths visible, infrared and radio are being combined to build a 3D model of its tail structure and outgassing behavior.
ALSO READ: ISRO Set to Launch India’s Heaviest Satellite CMS-03: A Boost for Naval Communication
Indian scientists using facilities like the Astrosat and Devasthal telescopes are at the forefront of analyzing the dust composition and light-scattering from the comet’s plume.
A Class Apart From ‘Oumuamua & Borisov
3I/ATLAS is an interstellar visitor unlike any other while ‘Oumuamua showed no signs of volatile activity, and 2I/Borisov appeared like any other long-period comet, 3I/ATLAS occupies a special place-it has a very stable orbit but an unusually high level of volatile activity. This makes it one of the rarest and most valuable test cases for studying how alien comets react to radiation from the Sun.
Now with 3I/ATLAS speeding on its path out of the inner solar system, scientists are racing against time to gather as much data as they can. What 3I/ATLAS reveals may forever change our understanding of the building blocks of life that drift between the stars.
ALSO READ: How Many Satellites Did Elon Musk’s SpaceX Launch in 2025? Can You Guess?
Disclaimer: This article is based on publicly available scientific data and space agency updates. Details may evolve as new observations emerge.