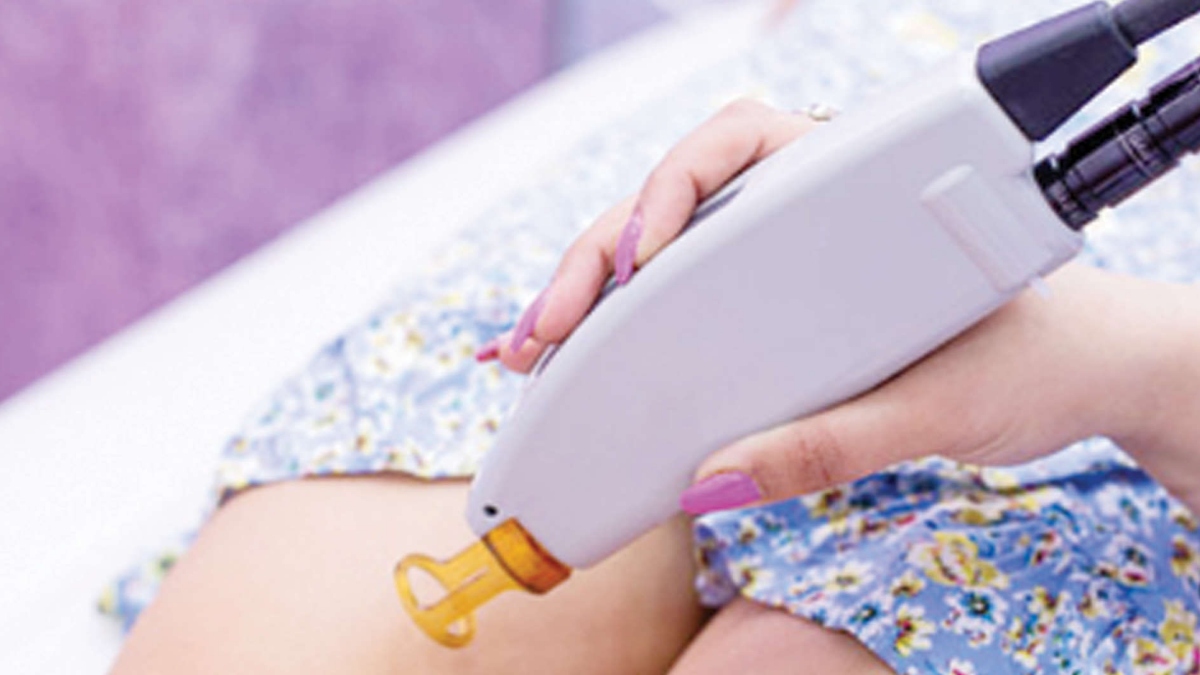
There are different types of medical lasers that are used in dermatology and cosmetology. Skin laser surgery has grown in leaps and bounds during the last 10 years. As new laser technology has evolved over the years, dermatologists have also helped define the specificity of laser-tissue interaction and have employed the newly developed laser technologies in innovative ways that further expanded the usefulness of these devices. One of the most important concepts to be developed by dermatologists selective photothermolysis has led to the creation of a series of laser systems that have provided numerous unique advantages in the management of many common vascular and pigmented conditions of the skin and mucous membranes, even in infants and children.
There are various types of lasers available on the market for different cosmetic and core dermatological problems, but a common man should be aware of the types of lasers, which one is the best for his/her problem, the expected cost of the entire therapy, duration of therapy, outcome (degree of beneficial effect), and the adverse effects of lasers.
The cost of laser therapy for different indications varies from Rs. 1500 to Rs. 3000 per session. But one should not get over-excited, seeing the advantages of lasers, lights, and other newer therapies.
The one thing patients suffering from skin and cosmetic ailments should =understand is that a mere one session of laser or light therapy won’t cure their problem. The key lies in being regular during the whole course of treatment.
The treating physician/surgeon and patients should also be aware of the conditions in which a patient cannot have laser therapy, like if they are on isotretinoin therapy, herpes virus infection, keloidal tendency, and abnormal endocrine status, etc.
An important word of caution is that lasers in the hands of inexperienced or unqualified people can prove disastrous. The greatest change is that these laser treatments are now affordable and approachable in India. Since the cost of skin and laser surgeries abroad is very costly, it’s also encouraging patients from abroad, especially NRIs, to come and have treatment here, thus increasing medical tourism.
The older continuous wave lasers used for skin surgeries were the continuous wave lasers like the carbon dioxide and argon lasers. However, the side effect of scar formation was unacceptably high with these lasers. The new lasers that have been introduced during the last two decades are comparatively safe and much more effective compared to the older versions.
The lasers differ according to the medium used in each laser. The characteristics of wavelength, pulse durations, and absorption by different chromophores within the skin determine the use and clinical applications of different types of lasers in dermatology.
Usage of Lasers and Lights in Dermatology
CO2 lasers: The laser light from these lasers is absorbed by water in the skin, hence, they are used for skin resurfacing, reduction of benign skin tumours, warts, xanthelasma, mucous cysts, cherry angiomas, leukoplakia, and surgical cutting.
Nd: YAG Lasers: The active medium is neodymium in yttrium-aluminum-garnet and the wavelength is 1064 nm. NdYAG lasers have slight absorption in melanin and haemoglobin and are used for laser hair reduction, laser vein treatments, laser photo rejuvenation, laser acne treatments, and laser skin surgeries.
Switched NdYAG Lasers have strong absorption in dark tattoo inks and are hence used in laser tattoo reduction.
Er. YAG Lasers: A wavelength of 2940nm and the active medium is Erbium in yttrium-aluminum-garnet. It is absorbed by water in the skin and is used for skin resurfacing, laser photo-rejuvenation, and reduction of skin growth.
Ruby lasers: A wavelength of 694 nm and contain chromium ions in aluminium oxide as the medium. Ruby laser light has very strong absorption in melanin and black and dark blue ink pigments.
These are especially useful in tattoo reduction. Laser hair reduction and reduction of pigmented (dark) skin lesions.
KTP, or Potassium Titanyl Phosphate Laser: with a 532 nm wavelength is a frequency-doubled NdYAG laser with absorption by haemoglobin and melanin and is used to remove vascular and pigmented skin lesions.
Alexandrite Lasers: 755 nm, Q switched mode laser, used to remove blue, black, and green tattoos and epidermal and dermal pigmentations as in melasma.
Diode Lasers: With different wavelengths the absorbing chromophores are melanin and haemoglobin in the skin. Diode lasers are used for laser hair reduction, dilated vein treatments, and laser photo-rejuvenation.
Dye lasers: Contain organic compounds in solution (often rhodamine) as the active medium and have wavelength activity between 400 and 800 nm.
The target chromophores are haemoglobin and melanin pigment. Dye lasers are useful in treating vascular lesions and for non-ablative skin rejuvenation.
Excimer laser: Contains compounds of xenon, krypton, and argon that target proteins and water and has wavelengths of between 190 and 350 nm. Excimer lasers are useful in the treatment of psoriasis and vitiligo.
Fractional lasers: The latest lasers that produce microscopic treatment zones and target specific depths in the dermis.
These are especially useful for the treatment of acne scars, wrinkles, sun-damaged skin, melasma, etc. The wavelength is in the range of 1550 nm, and the target chromophore is water within the tissue.
Intense Pulsed Light: (IPL-First Generation and Second Generation) is a technology aimed at producing light of high intensity during a very short period of time.
It involves specific lamps together with capacitors whose rapid discharge provides the high energy required. It is useful for hair reduction, acne, and Skin Rejuvenation.
NARROW BAND & UV-A UV-B: A technology aimed at targeting the affected skin cells using light of wavelengths 320-400nm and 311nm, respectively. It is used for the treatment of eczema, psoriasis, and vitiligo.
It is critical to understand which laser is best suited to your skin type and cosmetic issue.
The effects of laser energy on different structures of the skin depend upon the wavelength the power density, and the temperature characteristics of the laser.
Patient education on pre-and post-laser care will optimise results and decrease the incidence of adverse effects.
Finally, it’s important to note that one should not get over-excited and over-dependent on lasers, as lasers have lots of limitations too. Lasers do not produce the same result for the same disease in all individuals since everyone has a different cell type and behaviour. It can produce excellent results as desired by both the physician and the patient in
The author is EX- PGI, Chief Consultant Dermatologist & Dermato-Laser Surgeon
National SKIN HOSPITAL Panchkula.