The constant drive to improve human quality of life has resulted in tremendous developments and revolutions in the field of knee arthroplasty over the last several decades. The ever-increasing average life expectancy has demanded the investigation of novel approaches to the customization of implant architecture and material composition, which are precisely customized to individual patients. These factors are thought to contribute to the accurate restoration of knee alignment, increased material durability, and the prevention of short- or long-term problems associated with traditional implants.
In recent years, three-dimensional (3D) printing has witnessed notable addition which includes patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) and custom-made implants. As a result, more tailored implants and tools are now conceivable, resulting in improved accuracy during surgical procedures, whether in situations of degenerative knees or complex anatomical geometries where standard equipment may prove ineffectual.
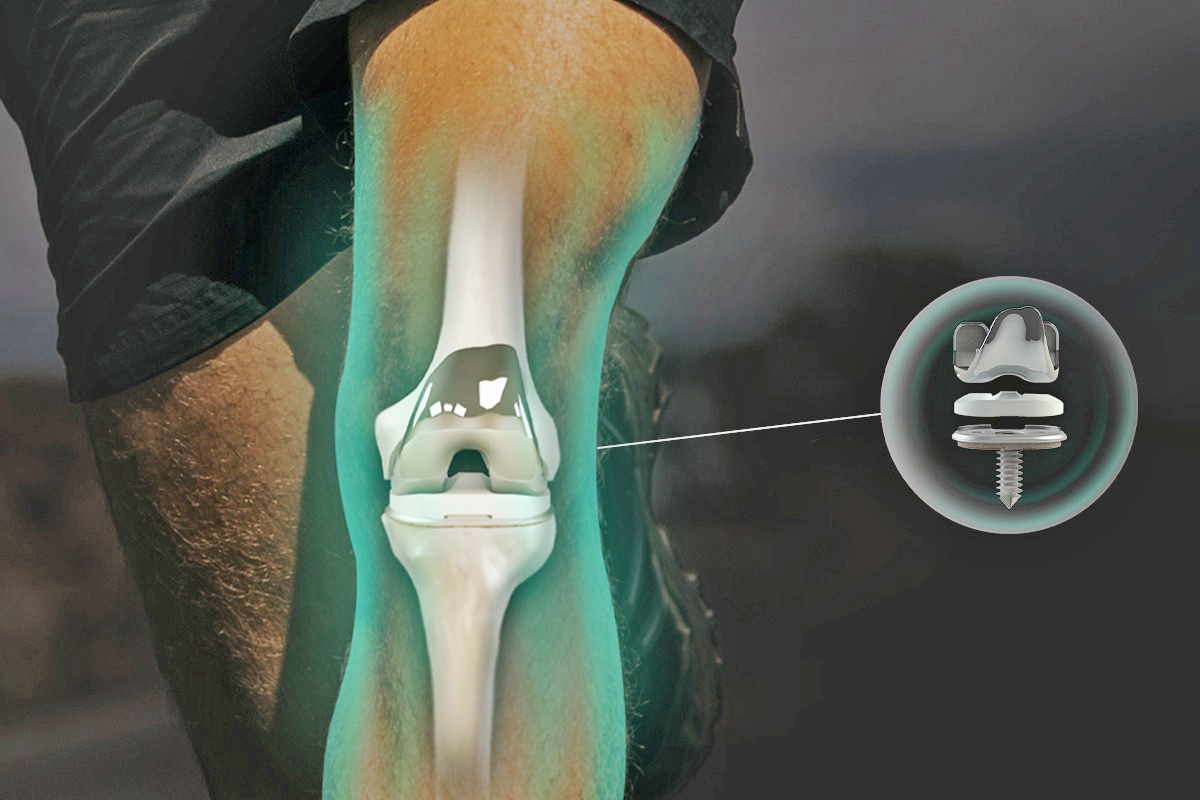
3D Printed Prosthetics
The success of total knee arthroplasty (knee replacement) depends significantly on accurate knee joint measurements, which can differ among individuals with degenerative conditions like advanced knee osteoarthritis. In traditional knee arthroplasty, surgeons typically rely on standardized measurements instead of obtaining patient-specific ones. Consequently, about 35% of patients undergoing traditional total knee arthroplasty seek a revision procedure within the initial two years.
Recently, medical professionals have pursued more personalized methods for knee replacement surgeries to better address patients’ specific needs. One prevalent method, known as patient-specific instrumentation, employs surgical guides derived from 3D CT or MRI data. These guides aid in customizing knee replacement procedures for individual patients.
Unlike traditional custom-made prosthetics, 3D printed prosthetics boast nearly 100% accuracy and can be fully tailored to match a patient’s unique anatomy. 3D printed knee replacements leave no margin for ill-fitting issues, positioning them as the top choice among available options for knee replacements.
Similar to other customized prosthetics, a precise 3D image of the knee is generated on a computer using a compilation of 2D knee images. This image is then three-dimensionally printed, creating an incredibly precise replica of the patient’s knee joint. This kind of prosthetic typically eradicates complications arising from poorly fitting replacements.
Benefits of 3D Knee Technique
The 3D knee replacement technique has demonstrated superior accuracy and effectiveness compared to other surgical methods. Pre-reviewing surgical procedures and implants beforehand significantly reduces operation time and minimizes the risk of infections. Various manufacturers now offer 3D implants, allowing patients and surgeons to compare different options and select the most suitable fit for each individual’s bone structure.
This approach emphasizes patient-centered care by enabling customized implants based on patient preferences, all of which can be evaluated before the surgery. Additionally, 3D technique implants can be inserted into the bone structure without the need for cutting or drilling surrounding bones, thus eliminating the likelihood of fat embolism.
Moreover, this 3D knee imaging technique is more cost-effective when compared to other robotic knee replacement surgeries, making it a more accessible option for patients.
Road ahead
This revolutionary surgery represents the future of implant procedures, setting a benchmark in multiple medical fields exploring 3D printing. Knee replacements have surged ahead, being readily available to patients. These surgeries boast the highest success rates, offering quicker recovery times and improved prosthetic functionality compared to traditional joint replacements.
Anticipated advancements in 3D printing techniques will likely incorporate cellular components to replicate fully functional knee parts, including cartilage, bone, and muscle. The potential integration of stem cell therapy aims to prevent prosthetic rejection, promising enhanced efficacy for these future techniques.
The author is the managing director at Aakash Healthcare Super Specialty Hospital.