In the rapidly advancing world of medical technology, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an essential tool in enhancing diagnostic accuracy and predicting treatment outcomes. Among the innovations driving these changes is the development of AI-powered glucose analysis, with GPT-4 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4) emerging as a promising player in this field. By utilizing vast amounts of data and offering powerful predictive capabilities, GPT-4 has opened new doors for more efficient and accurate glucose monitoring, helping patients and healthcare providers manage diabetes more effectively. However, despite its significant potential, the technology still faces several challenges and requires refinement to reach its full potential.
The Need for AI in Glucose Monitoring
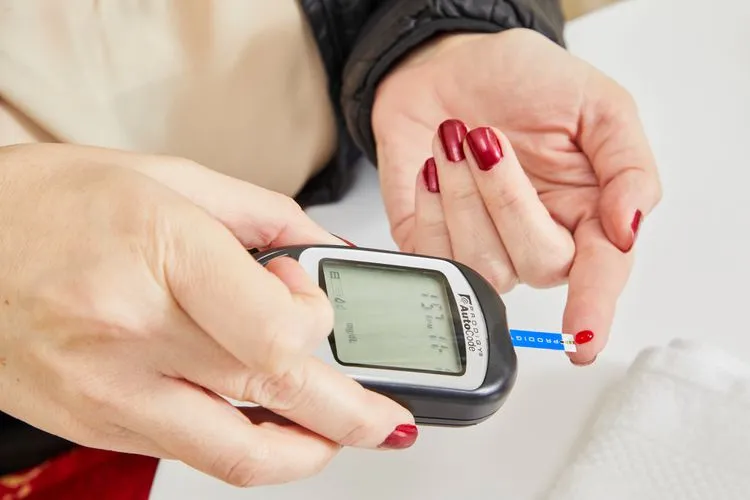
Diabetes, one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide, affects millions of people each year, with the prevalence of Type 2 diabetes continuously rising. Effective management of glucose levels is critical for preventing complications such as cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage, kidney failure, and even amputations. Traditional methods of glucose monitoring, such as fingerstick blood tests and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), have their limitations in terms of accessibility, accuracy, and real-time data analysis.
The challenge lies in interpreting glucose levels dynamically throughout the day, as fluctuations can result from various factors, including physical activity, stress, food intake, and medication. This calls for a more personalized approach to glucose management, one that can integrate multiple data points and provide timely predictions to help individuals adjust their treatment plans accordingly.
This is where AI comes into play, specifically through GPT-4’s ability to analyze vast datasets and learn from patterns within them. The promise of AI-powered glucose analysis lies in its potential to offer continuous, real-time, and personalized feedback, thereby improving the quality of care for individuals with diabetes and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
How GPT-4 Works in Glucose Analysis
GPT-4 is a state-of-the-art natural language processing model developed by OpenAI. While its primary use has been in text generation, its applications extend beyond the realm of linguistics, including healthcare. In the case of glucose monitoring, GPT-4 is capable of analyzing large datasets from CGMs, electronic health records, and wearable devices that track lifestyle habits, food intake, exercise, and other pertinent data.
By drawing on the collective power of these data streams, GPT-4 can generate insights about an individual’s glucose levels, predict future trends, and even recommend personalized interventions. Unlike traditional models, GPT-4’s deep learning capabilities enable it to identify subtle, complex patterns in glucose data, potentially offering insights that are difficult for human clinicians to recognize.
For instance, GPT-4 can predict how an individual’s glucose levels will fluctuate based on upcoming events—such as a meal, workout, or medication adjustment—by understanding the interactions between various factors. In this way, the AI can provide early warnings for potential glucose spikes or dips, empowering users to take proactive steps in managing their condition.
The Benefits of GPT-4 in Glucose Management
- Personalized Recommendations: One of the primary advantages of AI-powered glucose analysis is its ability to generate personalized recommendations based on an individual’s data. Unlike traditional methods, which typically rely on generalized guidelines, GPT-4 can tailor its predictions and suggestions to the unique needs and circumstances of the patient. This level of personalization helps in optimizing treatment plans and improving overall management of diabetes.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts: With continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data feeding into the AI model, GPT-4 can provide real-time monitoring and alerts when glucose levels are expected to become problematic. This could be particularly useful for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, who must make frequent adjustments to their insulin doses. By receiving timely warnings, patients can take action before their glucose levels rise or drop to dangerous levels, thereby avoiding emergencies.
- Improved Long-Term Outcomes: Studies have shown that tight glucose control—maintaining blood glucose levels within a healthy range—significantly reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications. By providing predictive insights and personalized recommendations, GPT-4 can assist in achieving better long-term outcomes by optimizing glucose control and minimizing the risk of complications over time.
- Time-Saving for Healthcare Providers: The application of GPT-4 in glucose analysis may also help healthcare providers streamline their workflow. By using AI to analyze large datasets, doctors can quickly access actionable insights without manually sifting through mountains of data. This can lead to more efficient decision-making, reduced burnout for clinicians, and better patient care.
Challenges and Areas for Refinement
Despite the promise of GPT-4 in glucose monitoring, there are still several challenges that must be addressed before it can be fully implemented in clinical practice.
- Data Quality and Accuracy: AI models, including GPT-4, are only as good as the data they are trained on. In the context of glucose monitoring, inaccurate or incomplete data could lead to incorrect predictions or recommendations. Moreover, as GPT-4 relies on large datasets, the accuracy of its analysis depends on how well the model has been trained to account for various factors affecting glucose levels, such as exercise, stress, and meal timing.
- Integration with Existing Technologies: While GPT-4’s ability to analyze a wide range of data is an asset, integration with existing monitoring technologies is essential for smooth implementation. Wearable devices, CGMs, and other health-monitoring tools must be compatible with GPT-4, and healthcare systems must ensure that these devices communicate seamlessly with the AI model. Otherwise, the AI’s predictions may be delayed or less accurate, undermining its effectiveness in real-time decision-making.
- Ethical Concerns and Privacy: The use of AI in healthcare raises significant ethical concerns, particularly around privacy and data security. In the case of glucose analysis, AI systems like GPT-4 would require access to sensitive health information, including glucose levels, medication history, and lifestyle habits. Ensuring the privacy of this data and adhering to regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is critical in maintaining trust in AI-driven healthcare solutions.
- Over-Reliance on AI: While AI-powered tools can offer valuable insights, there is a risk that patients or healthcare providers might become over-reliant on these systems. It is essential for users to understand that AI tools, including GPT-4, should complement—not replace—human expertise. Proper training and education will be necessary to ensure that healthcare providers and patients know how to use AI-generated recommendations effectively, without disregarding clinical judgment.
- Cost and Accessibility: While AI technologies like GPT-4 have the potential to reduce healthcare costs in the long run by improving efficiency and outcomes, the initial costs of implementing AI-powered systems could be prohibitive for some healthcare facilities, particularly in low-resource settings. Ensuring that AI tools remain affordable and accessible to all patients, regardless of their socioeconomic status, will be a critical hurdle for the widespread adoption of this technology.
The Future of AI-Powered Glucose Monitoring
As AI technology continues to evolve, so too will its applications in healthcare. GPT-4 and similar models are likely to improve over time as they are exposed to more data and as machine learning algorithms become more refined. In the future, AI-powered glucose monitoring systems could become even more accurate, reliable, and accessible, offering real-time predictions with greater precision.
Moreover, with the growing adoption of wearable health technology and advancements in personalized medicine, the integration of AI models like GPT-4 will play an increasingly central role in managing chronic conditions like diabetes. By seamlessly combining real-time glucose data with predictive insights, healthcare providers will be able to offer more tailored, effective treatment plans that reduce the burden of diabetes and improve patient quality of life.
In conclusion, GPT-4-powered glucose analysis represents a significant advancement in the field of diabetes care. By offering personalized predictions, real-time monitoring, and streamlined workflows, AI-powered tools hold immense promise in improving the management of glucose levels and reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. However, challenges such as data accuracy, integration with existing technologies, and ethical concerns must be addressed to fully realize the potential of this technology. As AI continues to evolve, its role in healthcare, particularly in glucose monitoring, is expected to grow, offering new opportunities for improving patient outcomes and transforming the landscape of chronic disease management.