India has made a significant stride in cancer treatment with the development of its first indigenous CAR-T cell therapy, NexCAR19. This groundbreaking therapy, tested on patients suffering from B-cell leukaemia and lymphoma—two rare blood cancers affecting the bone marrow and lymphatic system—has shown an impressive 73% success rate in clinical trials. Developed through a collaboration between the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay and Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai, NexCAR19 represents a beacon of hope for cancer patients in India, offering an affordable and effective treatment option.
Understanding CAR-T Cell Therapy
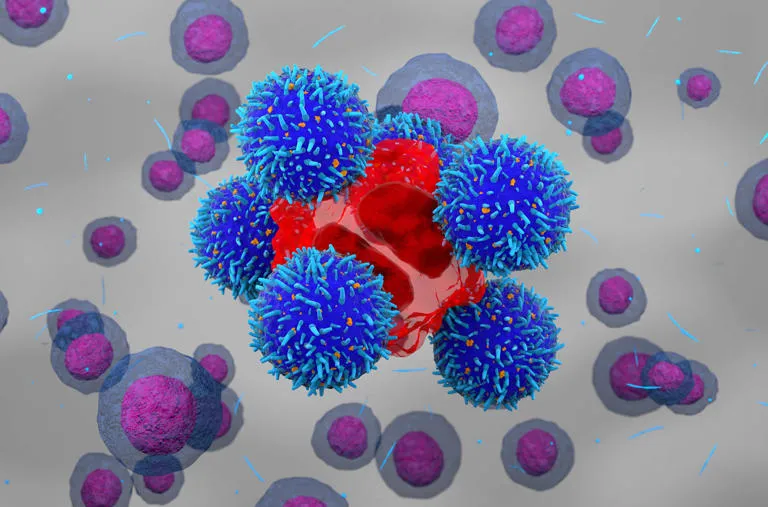
CAR-T cell therapy is an advanced form of immunotherapy, where a patient’s own T cells (a type of immune cell) are modified to target and destroy cancer cells. The process involves extracting T cells from the patient’s blood, genetically modifying them in a laboratory to recognize specific cancer antigens, and then reintroducing these engineered cells into the patient’s bloodstream. These modified cells are designed to bind to cancer antigens and kill the cancer cells effectively.
Dr. Alka Dwivedi, one of the researchers involved in the development of NexCAR19, explained that the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) on the T cell’s surface is crucial for recognizing and attacking cancer cells. Once the modified CAR-T cells encounter cancer cells expressing the specific antigen, they bind to them and initiate the cell-killing process.
The Clinical Trial and Its Outcomes
The clinical trial for NexCAR19 was conducted over two phases:
- Phase 1: Included 14 patients with relapsed or treatment-resistant B-cell lymphoma.
- Phase 2: Involved 50 patients diagnosed with either B-cell leukaemia or B-cell lymphoma.
The average age of the patients was 44 years, with a participant pool of 49 men and 15 women. The study, published in The Lancet Haematology, revealed that 73% of the 51 patients responded positively to the treatment, marking a substantial success in India’s cancer treatment landscape.
Despite the promising results, the therapy did pose some challenges. Two patients died due to treatment-related complications, and others experienced side effects such as neutropenia (low white blood cell count), thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), and anemia (reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood). However, the researchers concluded that the therapy is generally safe and offers long-term benefits for patients.
The Development Journey of NexCAR19
Developed over 11 years, NexCAR19’s journey involved rigorous research, lab testing, and extensive patient trials. The Indian drug regulator, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), approved the therapy in October 2013, recognizing its potential to offer an affordable cancer treatment option.
A key advantage of NexCAR19 is its cost-effectiveness. In the United States, similar CAR-T cell therapies cost between $373,000 to $475,000 (approximately Rs 3-4 crore), with total costs exceeding $1 million (Rs 8 crore) when care and associated expenses are considered. In stark contrast, NexCAR19 is priced at around $30,000 (Rs 25 lakh), making it more accessible to a larger section of India’s population.
Prof. Rahul Purwar from IIT Bombay, who played a pivotal role in developing the treatment, emphasized that NexCAR19 offers new hope for patients battling aggressive blood cancers. Dr. Hasmukh Jain from Tata Memorial Hospital added that the therapy’s ability to remain in the body for extended periods helps prevent relapses, a significant advantage over traditional cancer treatments.
Addressing Cancer Treatment Challenges in India
India faces a considerable challenge in providing effective cancer treatments, particularly for relapsed or treatment-resistant B-cell tumors. In low- and middle-income countries, including India, access to advanced cancer therapies is limited due to high costs and lack of availability. NexCAR19 aims to bridge this gap, providing a viable treatment option for patients who otherwise struggle to access advanced care.
Cancer affects B-cells—a type of white blood cell crucial for the immune response—making treatment complex and challenging. Traditional therapies like chemotherapy and radiation often come with severe side effects and high costs. The introduction of CAR-T cell therapy represents a paradigm shift, focusing on harnessing the body’s immune system to fight cancer more effectively.
Safety and Efficacy of NexCAR19
One of the critical aspects of NexCAR19 is its safety profile. The therapy incorporates human proteins in its mouse antibodies, reducing the likelihood of adverse immune reactions, particularly cytokine release syndrome, which can occur when the immune system releases excessive signaling proteins. Dr. Dwivedi highlighted that this modification ensures the therapy’s effectiveness against tumors while minimizing side effects.
The clinical trial’s high response rate—73%—is a testament to the therapy’s efficacy. However, the occurrence of side effects like neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia necessitates careful monitoring during and after treatment. The study’s findings concluded that despite these challenges, NexCAR19 is a safe and effective option for Indian patients, offering hope to those who previously had limited treatment choices.
Future Directions: Expanding CAR-T Cell Therapy
With the success of NexCAR19 in treating relapsed and treatment-resistant B-cell cancers, researchers are optimistic about expanding the therapy’s use. Dr. Jain mentioned that the next phase of research would involve testing NexCAR19 at earlier stages of cancer and exploring its combination with other treatments to enhance results.
New clinical trials are already underway at Tata Memorial Centre, focusing on these objectives. By integrating CAR-T cell therapy with other cancer treatments, researchers aim to improve overall survival rates and enhance the quality of life for cancer patients.
Implications for India’s Healthcare Landscape
The approval and successful testing of NexCAR19 mark a significant milestone in India’s healthcare sector. It underscores the potential of indigenous research and innovation in addressing complex healthcare challenges. The therapy’s affordability and high efficacy could transform cancer care in India, particularly for patients who previously had limited access to advanced treatments.
Dr. Jain stressed the importance of continuing research and increasing awareness about advanced cancer therapies. Greater public awareness and easier access to treatments like NexCAR19 could significantly reduce cancer-related mortality in India.
Moreover, the development of NexCAR19 showcases India’s growing capabilities in the field of biotechnology and gene therapy. It sets a precedent for future innovations in cancer treatment and other areas of healthcare, aligning with the government’s vision of making India a hub for affordable and advanced medical treatments.
Global Perspective: CAR-T Therapy on the Rise
Globally, CAR-T cell therapy has emerged as a revolutionary approach to cancer treatment. Countries like the United States and China have been at the forefront of CAR-T research, with several therapies already approved for use. India’s entry into this field with NexCAR19 positions the country as a significant player in the global cancer treatment landscape.
Studies suggest that Asia will witness a sharp rise in cancer cases, with an estimated 27.8 million additional cases by 2040. India and China are expected to be among the most affected countries. The success of NexCAR19 could serve as a model for other countries aiming to develop affordable and effective cancer therapies.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the promising results, challenges remain in scaling up the production and distribution of CAR-T cell therapies. The therapy requires advanced laboratory infrastructure, trained personnel, and a robust healthcare system to ensure that patients receive timely and effective treatment.
India’s healthcare system must address these challenges by investing in infrastructure, training healthcare professionals, and ensuring that therapies like NexCAR19 are accessible to patients across the country, including those in rural and underserved areas.
Awareness campaigns are also crucial to educating the public about the importance of early cancer detection and the availability of advanced treatments. As Dr. Asha M S from Nethradhama Super Speciality Eye Hospital highlighted the importance of routine check-ups for early detection in glaucoma, a similar approach can be adopted for cancer awareness and early detection.
The development and clinical success of NexCAR19 represent a significant achievement for India’s medical research community and offer renewed hope to thousands of cancer patients. With its high success rate, affordability, and potential to improve survival rates, India’s first homegrown CAR-T cell therapy marks a new era in cancer treatment.
As ongoing research seeks to expand its application and improve outcomes further, NexCAR19 could become a cornerstone in India’s fight against cancer, providing effective and affordable care to millions across the country.