The HEARTS Act, a significant legislative measure aimed at protecting students from the dangers of sudden cardiac arrest, was signed into law with a clear mission: to ensure that young individuals, particularly in educational settings, are provided with the tools and knowledge needed to respond to cardiac emergencies effectively. Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is one of the leading causes of death in young people, often occurring without warning and posing a significant challenge to those around the victim, especially in schools, sports events, and other youth activities. This legislation focuses on enhancing awareness, education, and preparedness to save lives when every second counts.
The Growing Concern: Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Youth
Sudden cardiac arrest is a medical emergency in which the heart unexpectedly stops beating. It can happen to anyone, regardless of age or health status, but it is particularly concerning in young individuals, often striking seemingly healthy children and adolescents. According to the American Heart Association, approximately 7,000 young individuals experience sudden cardiac arrest each year in the United States. The majority of these incidents occur during physical activities, such as sports, which is why schools, coaches, and athletic staff must be well-prepared to respond quickly and appropriately.
Key Provisions of the HEARTS Act
The HEARTS Act—an acronym for Helping Ensure Appropriate Response to Sudden Cardiac Arrest in Students—is designed to address the problem of sudden cardiac arrest in youth through several key provisions. The law focuses on improving awareness, creating guidelines for educational institutions, and ensuring access to life-saving equipment.
1. Mandatory CPR and AED Training
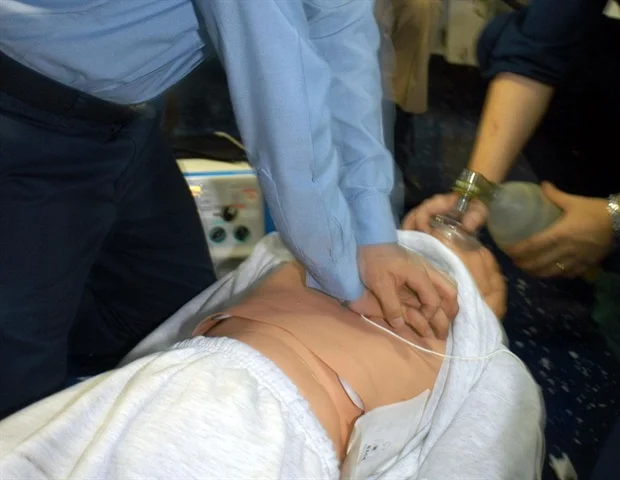
One of the most critical components of the HEARTS Act is its mandate for comprehensive training on CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) and the use of AEDs (automated external defibrillators) for teachers, coaches, and other staff members in schools. The law requires that these individuals be trained in basic life-saving techniques to help them respond effectively in an emergency. In many cases, immediate action—such as performing CPR or using an AED—can mean the difference between life and death.
2. Access to Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs)
The HEARTS Act ensures that every school has access to an AED. These devices are designed to administer a shock to the heart in the event of cardiac arrest, potentially restoring a normal heart rhythm. The law requires that schools not only have AEDs available on-site but also ensure that they are strategically placed and easily accessible. In addition, schools must ensure that staff members are trained to operate the devices effectively.
3. Creation of Sudden Cardiac Arrest Awareness Programs
The HEARTS Act includes provisions for the development and implementation of educational programs that raise awareness about sudden cardiac arrest. These programs are aimed at students, parents, and school staff to help them recognize the signs and symptoms of cardiac arrest and understand how to respond. Educating both young people and adults on the importance of recognizing cardiac emergencies is critical to ensuring quick action when needed.
4. Screening and Identification of At-Risk Students
In order to address the root causes of sudden cardiac arrest in young people, the HEARTS Act encourages schools to implement screening programs to identify students who may be at risk due to pre-existing heart conditions. The law recommends that schools collaborate with healthcare providers to offer regular screenings for heart conditions that can increase the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, such as arrhythmias, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and long QT syndrome.
5. Improved Emergency Response Plans
The HEARTS Act mandates that schools develop and implement clear emergency response plans for sudden cardiac arrest. These plans must outline the steps to take in the event of a cardiac emergency, including how to summon help, how to use the AED, and who is responsible for administering CPR. The law also stresses the importance of conducting regular drills to ensure that staff members are familiar with the procedure and can respond confidently and efficiently.
The Importance of Early Intervention
The most critical factor in surviving sudden cardiac arrest is the speed of the response. Research has shown that when CPR is administered immediately, the chances of survival increase significantly. The use of an AED within the first few minutes of a cardiac arrest can also dramatically improve the odds of survival. Studies suggest that early defibrillation can increase the survival rate by up to 75%. The HEARTS Act aims to reduce the time it takes to provide these life-saving interventions by ensuring that schools are well-equipped and well-trained to respond promptly.
Addressing the Risk in Schools
High school and college athletes are particularly vulnerable to sudden cardiac arrest due to the physical stress placed on their bodies during intense training and competition. In fact, a large percentage of sudden cardiac arrest cases in young people occur during or after physical exertion. For this reason, the HEARTS Act places particular emphasis on the role of sports coaches and athletic trainers in recognizing the early warning signs of cardiac distress and taking immediate action.
Through the HEARTS Act, schools are encouraged to implement comprehensive pre-participation physical evaluations (PPEs) for student athletes, including screening for cardiac conditions that could increase the risk of sudden cardiac arrest. These evaluations could include electrocardiograms (ECGs), which can help identify potential issues such as arrhythmias or heart abnormalities that might otherwise go undetected.
The Impact on Schools and Communities
The HEARTS Act has far-reaching implications not only for schools but also for communities as a whole. By raising awareness about sudden cardiac arrest, ensuring the availability of life-saving equipment, and providing proper training, the law helps foster a culture of preparedness. It ensures that educators, coaches, and students alike are empowered to take action in the event of a cardiac emergency. This proactive approach can save countless lives and provide reassurance to parents, knowing that schools are prepared to handle such emergencies effectively.
Moreover, the law acknowledges the importance of collaboration between schools, healthcare providers, and local emergency responders. Effective partnerships between these entities are essential to ensuring a coordinated and efficient response when sudden cardiac arrest occurs. The HEARTS Act encourages schools to work closely with local hospitals, emergency medical services, and other healthcare professionals to develop comprehensive response plans that integrate resources from all sectors.
The Legacy of the HEARTS Act
The signing of the HEARTS Act into law is a testament to the importance of protecting the health and safety of students. It represents a major step forward in the fight against sudden cardiac arrest and highlights the need for a multi-faceted approach to health and wellness in schools. With proper training, education, and resources, the risks associated with sudden cardiac arrest can be minimized, and the chances of survival can be greatly improved.
The HEARTS Act also serves as a reminder that sudden cardiac arrest does not discriminate based on age, physical fitness, or lifestyle. It can strike anyone, anywhere, and at any time. However, by equipping schools with the tools and knowledge needed to respond swiftly and effectively, the HEARTS Act offers hope for reducing the incidence of sudden cardiac arrest in young people and improving overall health outcomes.
Looking Ahead: Ensuring Continued Progress
While the HEARTS Act marks a significant achievement, it is important to continue to build on this progress. The next steps should include ongoing efforts to refine and improve the implementation of the law, ensuring that all schools have the resources they need to keep students safe. It is also essential to continue educating the public about the importance of heart health and the steps that can be taken to prevent cardiac emergencies.
As awareness grows, and as more schools implement the HEARTS Act’s provisions, it is hoped that the number of sudden cardiac arrest fatalities will decline. Through education, preparation, and swift intervention, we can work toward a future where the risk of sudden cardiac arrest in youth is significantly reduced, and lives are saved.
The HEARTS Act represents a groundbreaking effort to address the issue of sudden cardiac arrest in students, offering a comprehensive approach that combines education, awareness, training, and life-saving equipment. With its implementation, the law aims to ensure that schools are equipped to respond to cardiac emergencies quickly and efficiently, ultimately saving lives. By providing schools with the resources they need, and by educating students, staff, and parents, the HEARTS Act will help create a safer environment for young people, reducing the risks associated with sudden cardiac arrest and ensuring that help is always within reach.