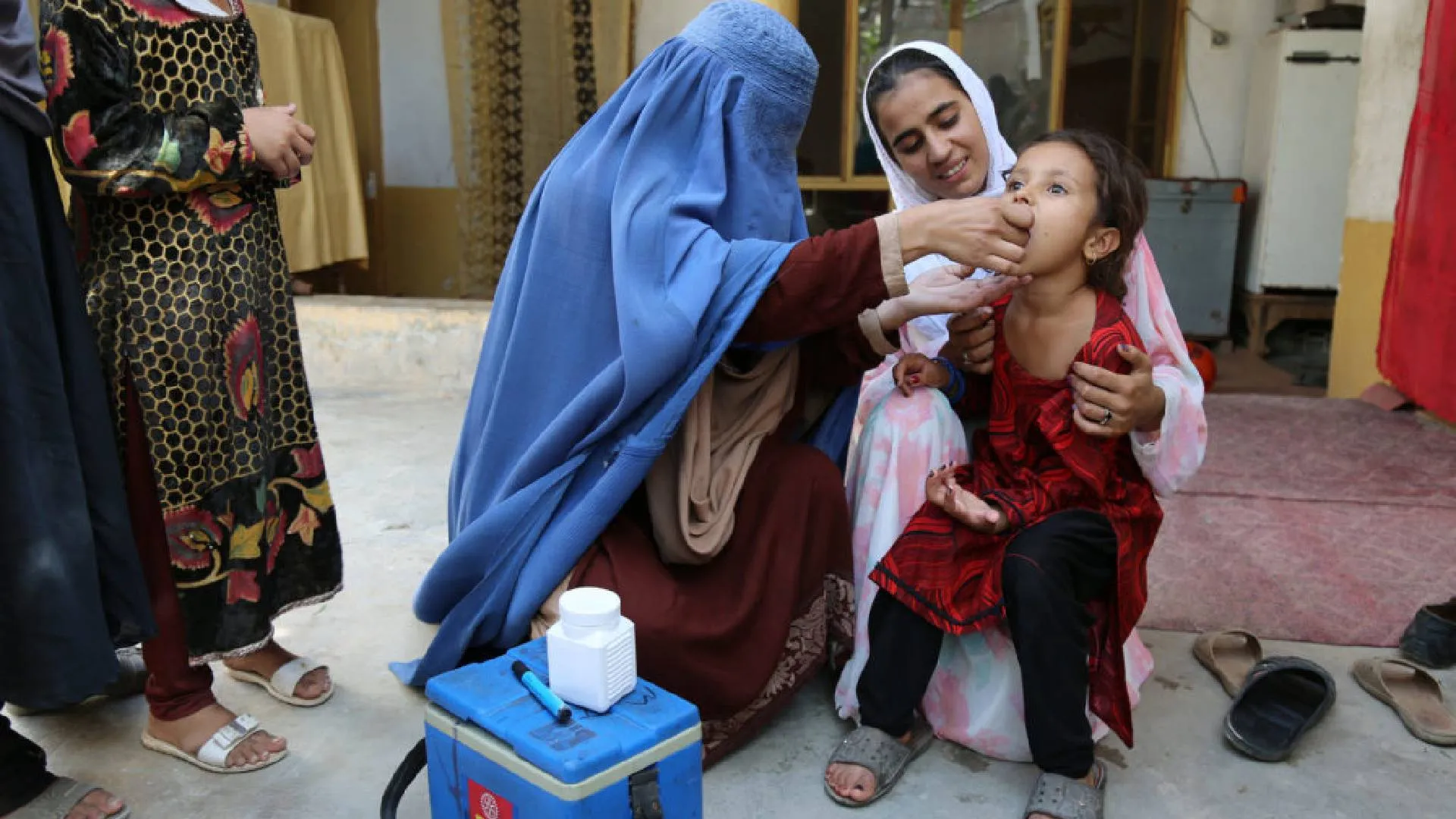
Immunisation is one of the tried and tested ways of protecting ourselves, our children, and future generations from infectious diseases. It basically helps us in the prevention and spread of disease, not only in the current situation but also in the future. It is the most common way of building the immune system of our body, even before we fall sick. Infants, children, teenagers, young adults, and adults also needs immunisations.
Importance of
Immunisation
When an infection occurs in an individual, they produce symptoms such as fever, cough, cold, etc., depending on the type of infection. Later, they recover or have complications and die, depending on reactions in the body. If the person survives and gets reinfection, symptoms are fewer or there are no symptoms if an antibody is present. So, infection is introduced into the body by the way vaccine antibodies are produced to protect.
Vaccines can be live, killed, proteins, or antigens. Certain vaccines are contraindicated for immunodeficiency conditions like HIV. Some people develop reactions or allergies. Hence, it is important that vaccinations be given with precaution.
immunisation is good for adults
It is a common belief that immunisation is required only for children. But it is equally important for adults too. It is a known fact that a lot of adults are susceptible to disease, and vaccination plays a very important role in adults. We may be at risk of disease due to our jobs, lifestyle, travel, and other health conditions. But immunisation plays a very important role in controlling and preventing disease from spreading. Vaccinations help to a great extent in lowering the chances of getting certain diseases and suffering from their complications. It works with our body’s natural immune system and helps it fight more effectively. As age advances, antibodies decrease, as in the case of diphtheria and pneumococcal disease. In the case of diphtheria, it is preferred to give a tetanus vaccine. Pneumococcal vaccines are also preferred in elderly adults to prevent serious complications.
In 2021, diphtheria cases in India were 17,688. Risk factors for developing infections are more common in people with diabetes, heart failure, kidney failure, and smokers. Also, in HIV-infected individuals, on dialysis, immunosuppressive medications, and transplant patients. Immunisation is one of the prominent and effective means and paths to improved health. Awareness of immunisation has taken centre stage only during the recent pandemic. I was under the impression that vaccinations were meant only for infants and children. There are myths surrounding vaccinations. The most common of them is that vaccines are not safe and that immunisation multiple times causes the risk of harmful side effects.
The truth is, the licensing of vaccines undergoes exhaustive evaluations and testing to ensure they are safe and effective. Post-release of vaccines after approval by the governing bodies like the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the Advisory Committee on Immunisation Practises (ACIP), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), etc.
The prevalence of diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, rabies, measles, rubella, mumps, and their complications has decreased drastically over the past two decades. Hepatitis B complications like chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as the spread of infection, are decreased by hepatitis B vaccination.
Seasonal influenza is an acute respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses A and B. It is contagious and can spread rapidly. H1N1, also known as swine flu, is a type of influenza A virus, and H1N1 is one of several flu virus strains currently causing seasonal flu across the country. The most effective way to prevent infections is vaccination. Thus, it is advisable for people to take a dose of the seasonal influenza vaccine to protect themselves from H1N1. WHO also recommends pneumococcal, influenza, and diphtheria vaccines along with the COVID-19 vaccine to prevent morbidity. To prevent suffering and complications of disease, it is recommended to immunize yourself with the advice of a doctor, for adults and for people in the elderly age group.
Dr Bindumathi P. L. is Sr.
Consultant, Internal Medicine