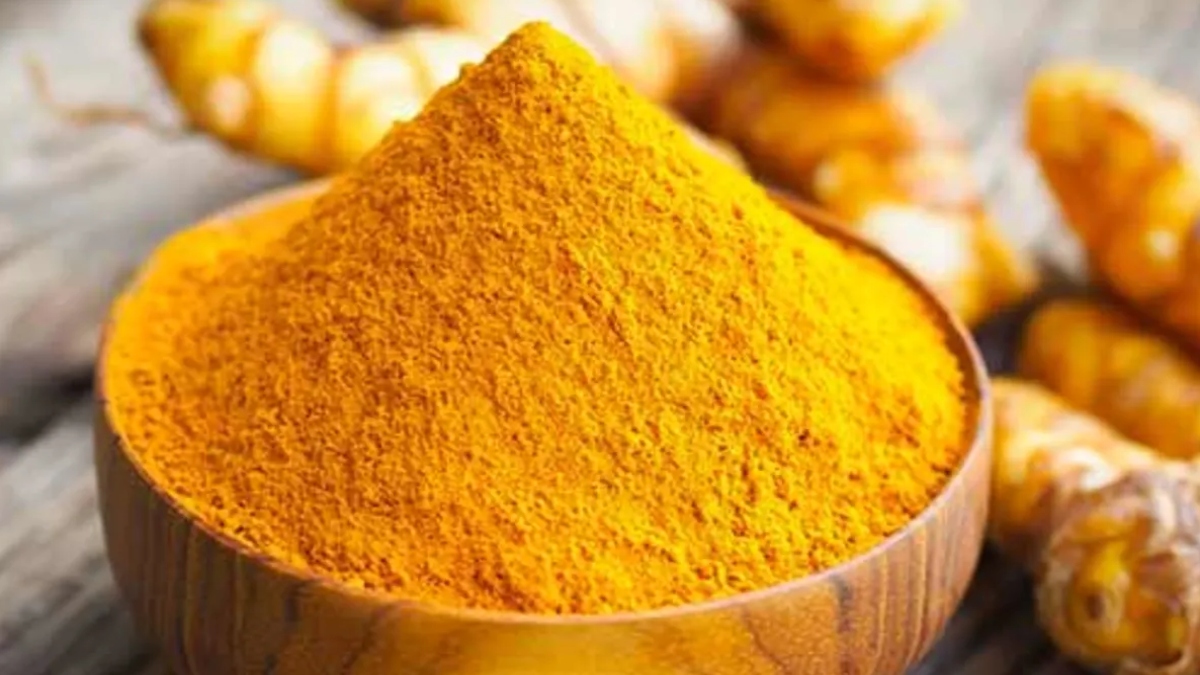
According to a new study by the University of California, a compound found in turmeric called Curcumin helps grow engineered blood vessels and tissues.
The findings of the study were published in the journal, ‘ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. The study indicated that a finding by UC Riverside bioengineers could hasten the development of lab-grown blood vessels and other tissues to replace and regenerate damaged tissues in human patients.
Curcumin has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties and is known to suppress angiogenesis in malignant tumors.
The magnetic hydrogels embedded with curcumin-coated nanoparticles promote the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factors.
Curcumin’s possible use for vascular regeneration has been suspected for some time but has not been well studied. Huinan Liu, a bioengineering professor in UCR’s Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering, led a project to investigate curcumin’s regenerative properties by coating magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles with the compound and mixing them into a biocompatible hydrogel.
Bioengineers at UC Riverside have now discovered that when delivered through magnetic hydrogels into stem cell cultures this versatile compound paradoxically also promotes the secretion of vascular endothelial growth factor, or VEGF, that helps vascular tissues grow.
When cultured with stem cells derived from bone marrow, the magnetic hydrogel gradually released the curcumin without injuring the cells.
Compared to hydrogels embedded with bare nanoparticles, the group of hydrogels loaded with curcumin-coated nanoparticles showed a higher amount of VEGF secretion.
“Our study shows that curcumin released from magnetic hydrogels promotes the cells to secrete VEGF, which is one of the most critical growth factors to enhance the formation of new blood vessels,” said co-author Changlu Xu, a doctoral candidate in Liu’s group who focused on hydrogel research.
The researchers also took advantage of the nanoparticles’ magnetism to see if they could direct the nanoparticles to desired locations in the body.
They placed some of the curcumin-coated nanoparticles in a tube behind pieces of fresh pig tissue and used a magnet to successfully direct the movement of the nanoparticles.
The achievement suggested the method could eventually be used to deliver curcumin to help heal or regenerate injured tissue.
In fact, the best curcumin supplements contain piperine, and this makes them substantially more effective.
In addition, animal and cellular studies suggest that curcumin may block the action of free radicals and may stimulate the action of other antioxidants. Further clinical studies are needed in humans to confirm these benefits