A total of 3,16,05,581 Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) were registered in India between July 1, 2020, and December 4, 2023, as reported by the Central government.
Minister of State for MSMEs Bhanu Pratap Singh Verma responded in writing when asked by a member about the total number of registered MSMEs in the country and the year-on-year increase and decrease in registration for the last five years.
Citing data uploaded on the Udyam Registration Portal, the Minister said all the 3,16,05,581 MSMEs included informal micro-enterprises. All the MSMEs were registered on the Udyam Assist Platform.
Verma also shared data that shows the registration of 28,47,544 MSMEs in 2020; 51,47,993 in 2021; 85,82,179 in 2022; and 1,50,27,865 in 2023.
In response to the query of Independent MP Kartikeya Sharma, the Minister further said the total number of women-owned MSMEs registered from July 1, 2020, to December 4, 2023, in the country was 1,17,36,406 (including informal micro-enterprises registered on Udyam Assist Platform).
Asked whether any steps have been taken by the government for resolution of the issue of pending payments faced by the MSME sector, Verma said the ministry has taken several steps in ensuring the growth of the MSME sector like “Udyam Registration” for MSMEs for Ease of Doing Business with effect from July 1, 2020, the inclusion of retail and wholesale traders as MSMEs with effect from July 2, 2021, for priority sector lending, and non-tax benefits extended for three years in case of an upward change in status of MSMEs with effect from October 18, 2022.
Launch of the Udyam Assist Platform on January 11, 2023, to bring Informal Micro Enterprises under the formal ambit for availing the benefits under Priority Sector Lending was among these steps, said the Minister.
On the steps taken by the government for resolution of the issue of pending payments faced by the MSME sector, the Minister said, under the provisions of the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, MSEFCs have been set up in the states and Union Territories (UTs) to deal with the cases of delayed payments of the MSEs. “The Ministry of MSME launched a portal viz. Samadhaan Portal for filing grievances and for monitoring the outstanding dues to the MSEs from the buyers of goods and services on
October 30, 2017. The Ministry of MSME has requested states and UTs to set up more MSEFCs for quicker disposal of cases related to delayed payments. So far, 157 MSEFCs have been set up with more than one MSEFC set up in States like Delhi, Gujarat, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal,” said the Verma.
The Ministry of MSME created a special sub-portal within the Samadhaan Portal on June 14, 2020, after the AatmaNirbhar Bharat announcements for reporting the dues and monthly payments by Central ministries, departments, and public sector enterprises to MSMEs, he said.
“The government of India has also instructed CPSEs and all companies with a turnover of Rs 500 crore or more to get themselves on-boarded on the Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS), an electronic platform for facilitating the discounting of trade receivables of MSMEs through multiple financiers,” stated the Minister.
As per the MoS, companies that get supplies of goods or services from MSEs and whose payment to MSEs exceeds 45 days from the date of acceptance or the date of deemed acceptance of the goods or services, also need to submit a half-yearly return to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs stating the number of payments due and the reasons of the delay.
“Under Section 43B of the Income Tax Act, deduction has been allowed for expenditure incurred on payments only when payment is actually made to MSMEs,” the Minister added.
WHAT IS MSME?
The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises is the governing body in the Government of India responsible for formulating and administering rules, regulations, and laws pertaining to micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs). The current Minister of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises is Narayan Rane.
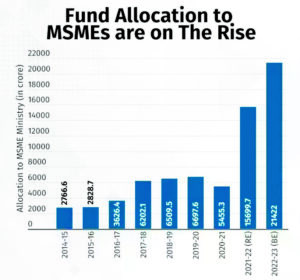
According to the annual reports of the Ministry of Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), there has been an increase in the plan amount allocated to the khadi sector from 1942.7 million to 14540 million, and non-plan amounts from 437 million to 2291 million, spanning the period from 1994–95 to 2014–2015. During this time, interest subsidies provided to khadi institutions rose from 96.3 million to 314.5 million.
MSME, which stands for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, is categorized into two divisions as per the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act of 2006: Manufacturing enterprises – involved in the manufacturing or production of goods in any industry. Service enterprises – engaged in providing or rendering services.
ESSENTIAL FEATURES OF MSMEs
MSMEs are known to provide reasonable assistance for improved access to the domestic as well as export markets for businesses
MSMEs support product development, design innovation, intervention, and packaging elements of a business
MSMEs support the upgrading of technology, infrastructure, and the modernization of this sector as a whole
MSMEs provide employment opportunities and loans
MSMEs provide credit limits or funding support to various banks in the country.
ROLE OF MSMEs IN THE INDIAN ECONOMY
The MSME sector has proven to be a highly dynamic factor in the forecasting of the Indian economy. Since MSMEs produce and manufacture a variety of products for both domestic as well as international markets, they have helped promote the growth and development of various product segments and industries.
MSMEs have played an essential role in providing employment opportunities in underprivileged areas. They have helped in the industrialization of such areas with a low capital cost compared to the larger industries in cities. MSMEs have also contributed and played an essential role in the country’s development in different areas like the requirement of low investment, flexibility in operations, low rate of imports, and a high contribution to domestic production.
KEY ANNOUNCEMENTS OF ATMA-NIRBHAR BHARAT ABHIYAAN
Rs 3 lakh crore collateral free automatic loans for MSMEs
Rs 50,000 crore equity infusion through MSME Fund of Funds
Rs 20 crore subordinate debt for MSMEs
Extension of registration and completion date of real estate projects under RERA
Immediate pending refunds issuance to all non-charitable trusts
Extension of the due date for ITR for FY’19-20 to November 30, 2020















