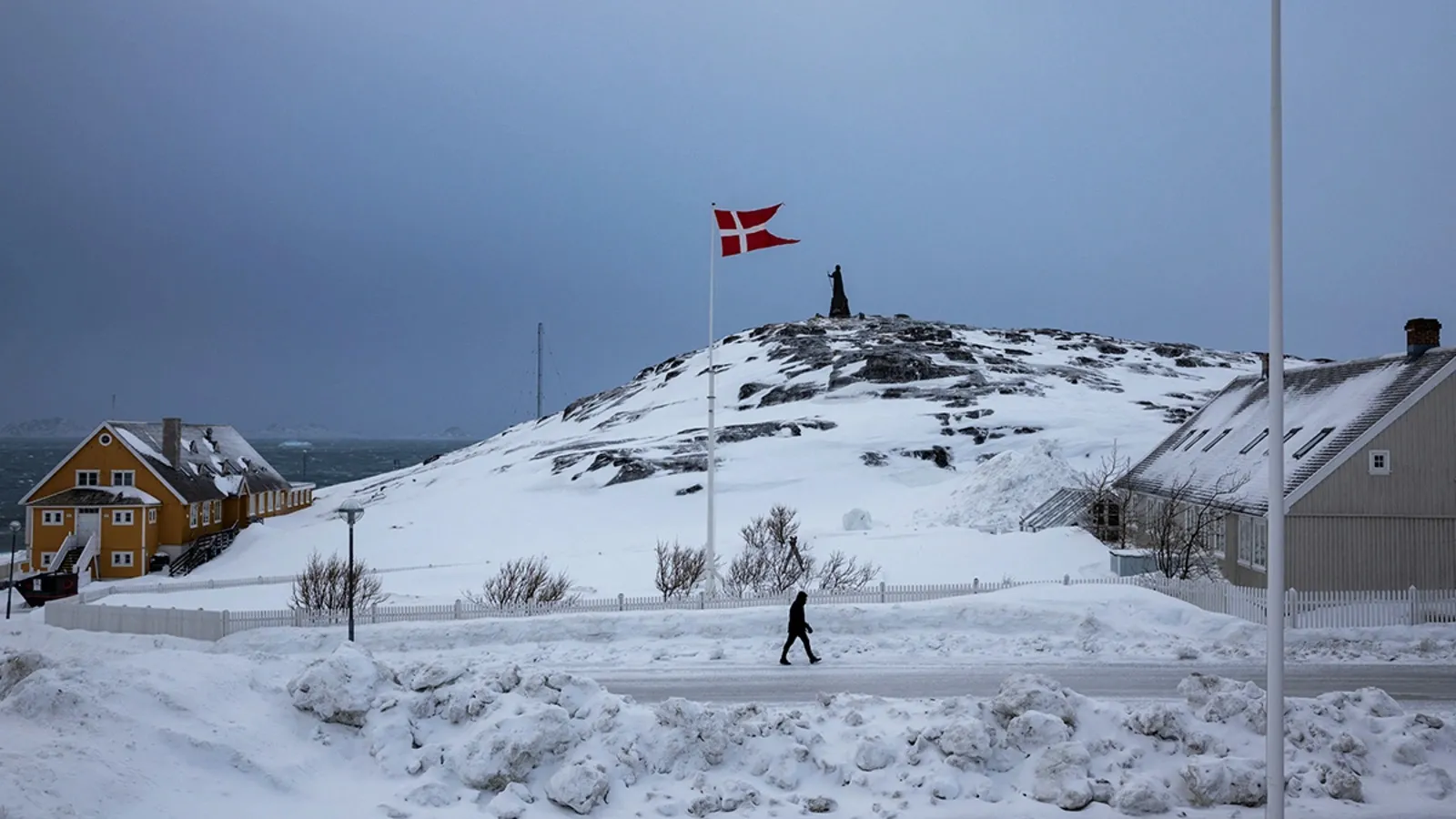
Greenland, the world’s largest island, has long held significant geopolitical importance due to its strategic location in the Arctic and its wealth of natural resources. As the movement for Greenland’s independence gains momentum, it presents a critical moment for the United States to reassess its interests and security concerns in the Arctic region. Greenland’s independence could significantly reshape U.S. policies, particularly in the realms of military security, economic opportunities, and geopolitical dynamics in the Arctic. The shifting political landscape raises questions about how the U.S. will adapt to this evolving situation.
Greenland’s Strategic Significance
Greenland’s geographical location has always made it a focal point in international geopolitics. Situated in the North Atlantic, Greenland holds a commanding position in the Arctic, an area of increasing global importance due to the effects of climate change, which are making previously inaccessible resources more reachable. The island is rich in rare earth minerals, oil, and gas, resources that are becoming increasingly vital to global industries, especially in technology, electronics, and renewable energy sectors.
In addition to its resource wealth, Greenland’s location offers strategic advantages for military and shipping interests. With climate change leading to the melting of Arctic ice, new sea lanes are opening up that could facilitate trade and military movement between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This growing accessibility of the Arctic region has attracted significant attention from both traditional and emerging powers, such as Russia and China, all vying for influence in this newly accessible part of the world.
U.S. Interests and Historical Context
The United States has long recognized Greenland’s strategic value. In 1946, the U.S. proposed purchasing Greenland from Denmark, although the offer was rejected. Over the years, Greenland’s role in U.S. security strategy has grown more prominent, particularly with the establishment of the Thule Air Base (Pituffik), a critical site for missile warning systems and space surveillance. The Thule Air Base remains essential for the U.S. military’s Arctic and global defense capabilities.
More recently, in 2019 and again in 2025, President Donald Trump expressed interest in purchasing Greenland, citing its geopolitical importance and rich resources. These proposals were firmly rejected by both Greenlandic and Danish officials, underlining Greenland’s strong desire for sovereignty and self-determination. The push for independence has only gained momentum in recent years, culminating in significant political changes in 2025.
Recent Political Developments in Greenland
In March 2025, Greenland held parliamentary elections that saw the pro-business Demokraatit party, led by Jens-Frederik Nielsen, emerge victorious. The party’s platform included a strong push for gradual independence from Denmark, focusing on domestic concerns like healthcare, education, and economic development. Nielsen’s stance on U.S. involvement in Greenland has been clear: he has firmly opposed any U.S. attempts to gain control over the island and stressed the importance of Greenland’s self-determination.
This political shift marks a pivotal moment in Greenland’s relationship with Denmark and its foreign policy direction. As Greenland moves toward greater autonomy, its relationship with the U.S. will likely evolve, requiring a careful balance of strategic interests, economic cooperation, and respect for Greenlandic sovereignty.
Implications for U.S. Interests
Military and Security Considerations
The U.S. maintains a significant military presence in Greenland, most notably the Thule Air Base, which plays a crucial role in missile warning systems, space surveillance, and Arctic defense. The base’s location provides the U.S. with strategic advantages in monitoring potential threats from Russia and other adversaries in the Arctic region.
Should Greenland gain full independence, it is likely that the U.S. would need to renegotiate its defense arrangements. The status of U.S. military installations, such as Thule, would be a key issue in future discussions. Greenland’s sovereignty would mean that the U.S. could no longer assume automatic access to these strategic military sites, potentially requiring a new defense treaty or security agreement to ensure continued cooperation in the Arctic.
Maintaining access to Greenland’s strategic locations would be critical for U.S. national security, particularly as the Arctic becomes an increasingly contested region. Any disruptions to U.S. military operations in Greenland could undermine the U.S.’s ability to respond to emerging threats in the region.
Resource Access and Economic Opportunities
Greenland’s vast natural resources, including rare-earth minerals, oil, and gas, are vital for global industries, particularly in the development of electronics, renewable energy technologies, and defense systems. With climate change opening up new access to these resources, Greenland’s economic potential has become more pronounced.
An independent Greenland could seek to diversify its economic alliances, possibly shifting away from Denmark and pursuing new partnerships with global powers, including the U.S., China, and Russia. For the U.S., this presents opportunities for investment, particularly in resource extraction and infrastructure development. However, any such cooperation would require navigating Greenland’s domestic regulations, which could involve significant environmental protections given the island’s fragile Arctic ecosystem.
Greenland’s economic independence would likely bring new challenges and opportunities for the U.S. While cooperation could drive economic growth, it would also require balancing economic ambitions with environmental concerns to ensure sustainable development in the Arctic.
Geopolitical Dynamics
The Arctic is increasingly becoming a focal point of international competition, particularly between Russia, China, and the United States. As the region becomes more accessible due to melting ice caps, countries are vying for influence over new trade routes and access to natural resources.
Greenland’s independence could significantly alter the balance of power in the Arctic. Without Denmark’s oversight, Greenland would have more control over its foreign policy, potentially opening the door for greater influence from China or Russia. For the U.S., this shift would require more diplomatic engagement to ensure that Greenland does not fall into the sphere of influence of strategic competitors.
An independent Greenland would also need to navigate complex issues related to Arctic governance, including territorial claims, resource rights, and environmental protections. The U.S. would need to work closely with Greenland to ensure that its interests in Arctic security, shipping routes, and resource access are not undermined by rival powers.