Image Source: AI
E-Governance in India involves the application of information and communication technology (ICT) by the government to provide services, exchange information, and facilitate transparent administration. It seeks to make the government work faster, easier, and more citizen-centric.
Through E-Governance, government procedures are computerized so that they have less manual intervention, less corruption, and are more accessible. The concept captures the overall national vision of "Minimum Government, Maximum Governance.".
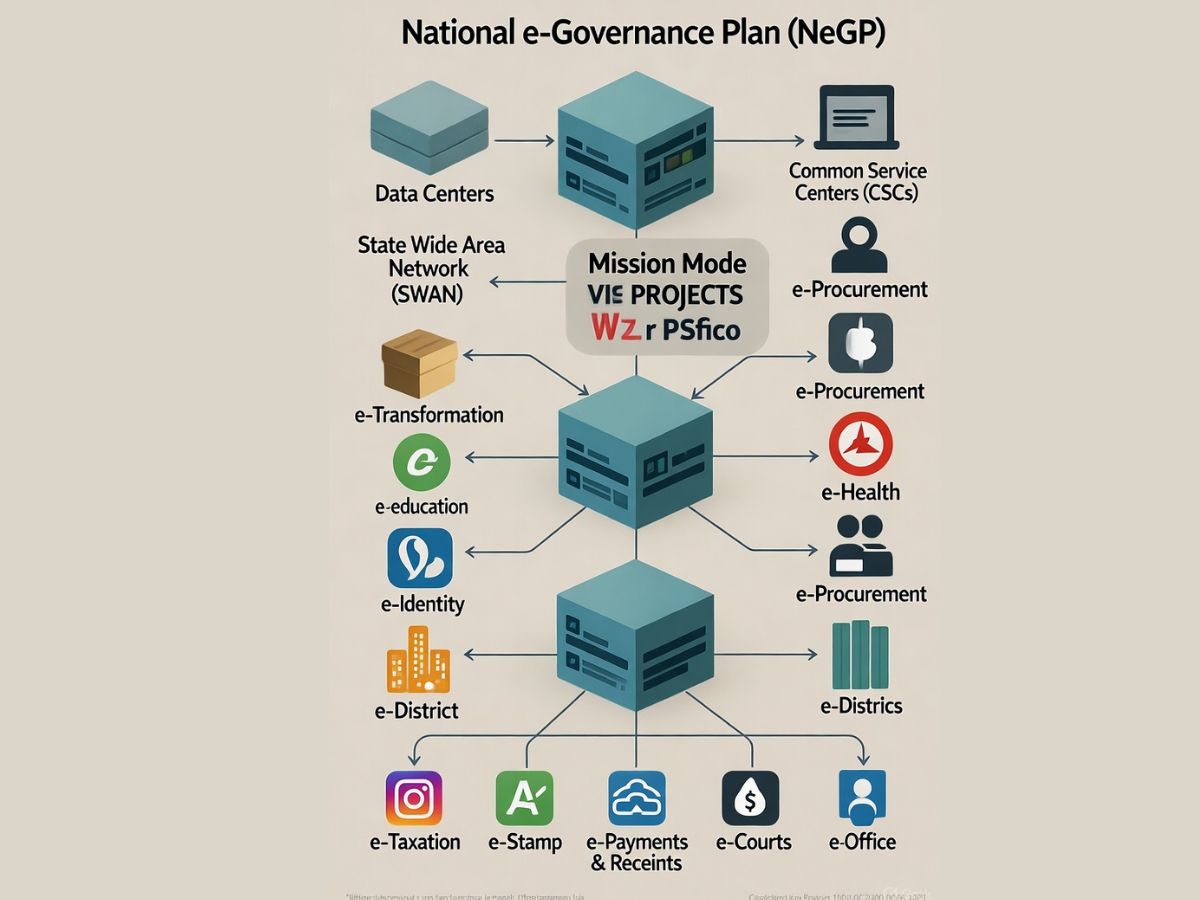
The Union Government cleared the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP), consisting of 27 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and 10 components on May 18, 2006. The NeGP focuses on enhancing delivery of Government services to citizens and enterprises.
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) looks at e-Governance initiatives countrywide from a holistic perspective, linking them to a common vision, a common purpose.
The National e-Governance Plan has added new initiatives like e-Pramaan and G-I cloud for authentication, and Social Media Framework & Guidelines for Government Organisations.
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) originally had 27 Mission Mode Projects. In 2011, 4 additional projects were included, bringing the MMP tally to 31.
e-Governance in India has progressively changed from computerization of Government Departments to initiatives that encompass the nuances of Governance, including citizen centricity, service orientation, and transparency.
The document mentioned a number of earlier initiatives as sources of inspiration, with quotes being made of the Singapore ONE programme. In an effort to achieve this objective, the National e-Governance Plan was developed by the Department of Information Technology (DIT) and Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances (DAR&PG).
Also Read. Can Trump Convince Putin to Halt the War Without Supplying Missiles?