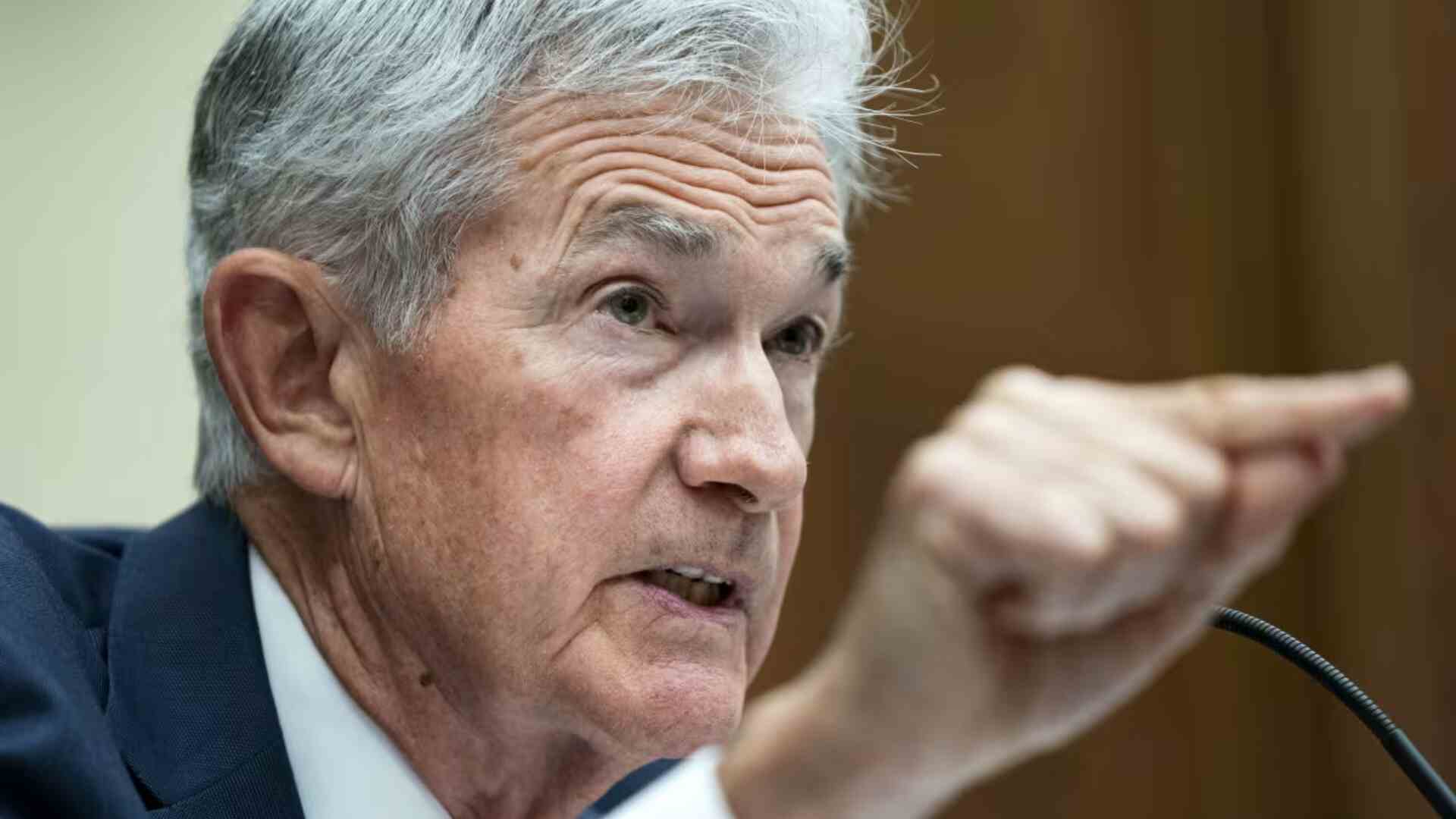
US Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell indicated on Friday that the central bank is poised to adjust its monetary policy, with potential rate cuts depending on upcoming inflation and unemployment data. Speaking at the Jackson Hole Symposium, Powell acknowledged that while inflationary risks have lessened, concerns about employment have increased.
Labor Market Conditions
“The labour market has cooled considerably. The unemployment is at 4.3 percent, which is still low by historical standards but still almost 4 percentage points above its level in early 2023,” Powell stated. He noted a decline in job vacancies and moderated nominal wage gains. Powell emphasized that labor market conditions are now less stringent compared to pre-pandemic levels in 2019, a period of low inflation. He assured that further cooling in the labor market is not desired.
Inflation and Employment Risks
Jerome Powell remarked, “The upside risks to inflation have diminished, and downside risks to employment have increased. As we have highlighted in our last FOMC statement, we are attentive to the risks of both sides.” He suggested that the Federal Reserve might initiate a rate cut cycle starting with a possible increase of up to 50 basis points in September 2024, contingent on evolving economic data.
Market Reaction
Following Powell’s remarks, the Nasdaq climbed 1.41 percent and the Dow Jones Industrial Average rose 0.78 percent. The US central bank has maintained interest rates steady for the past year since July 2023. Prior to that, the Fed had raised rates by 525 basis points between March 2022 and July 2023 to combat inflation, which spiked due to the Ukraine-Russia conflict and COVID restrictions.
The last rate cut occurred on March 15, 2020. The next Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting is scheduled for September 17-18, where further decisions on interest rates will be discussed.